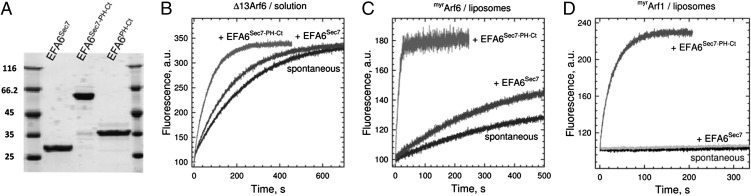
Fig. 1.
Regulation of Arf1 and Arf6 activation by EFA6 on membranes. (A) EFA6 constructs used in this study (12% SDS/PAGE, 3 μg/lane). (B) EFA6 is not autoinhibited by its PH-Ct domain. Representative tryptophan fluorescence kinetic traces for Δ13Arf6 (1 μM) activation in solution by EFA6 constructs (100 nM) as indicated. (C) EFA6 is strongly potentiated by membranes. Representative kinetic traces for myrArf6 (0.4 μM) activation by EFA6Sec7-PH-Ct (10 nM) or EFA6Sec7 (220 nM) in the presence of liposomes. (D) EFA6 is a potent Arf1GEF on membranes. Representative tryptophan fluorescence kinetic traces for myrArf1 activation by EFA6Sec7-PH-Ct (3.75 nM) or EFA6Sec7 (575 nM).