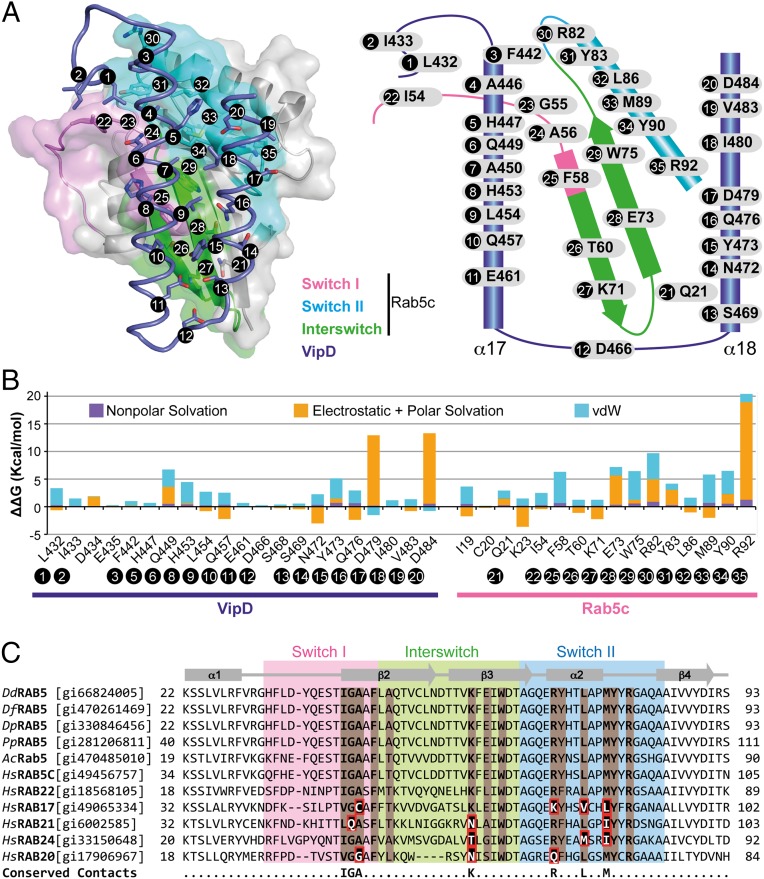
Fig. 3.
Molecular interactions at the VipD–Rab5c interface. (A) (Left) Semitransparent surface of GppNHp-Rab5c18–182 in complex with the minimal Rab binding domain of VipD (slate ribbon model) highlighting the interfacial residues below 4.0-Å distance. (Right) Schematic diagram of interfacial residues in the VipD–Rab5c complex. (B) Detailed description of per-residue contribution from van der Waals (vdW) energy (blue), nonpolar solvation energy (purple), and the sum of electrostatic and polar solvation energy (orange) calculated by computational alanine scanning for interfacial residues in the VipD–Rab5c complex. Existing glycines and alanines are excluded in the calculation. (C) Sequence conservation between Rab5 GTPases from amoebean species and human homologs. Dd, Dictyostelium discoideum; Df, Dictyostelium fasciculatum; Dp, Dictyostelium purpureum; Pp, Polysphondylium pallidum; Ac, Acanthamoeba castellanii; Hs, Homo sapiens. Rab5c residues contacting VipD at a distance less than 4 Å are colored in light brown. Amino acid substitutions within the equivalently aligned interfacial residues of other Rabs are highlighted in a red box. Interfacial residues strictly conserved between Rab5 and Rab22, but variable in any of the other Rabs, are depicted in the bottom line of the alignment. Protein accession numbers are in brackets.