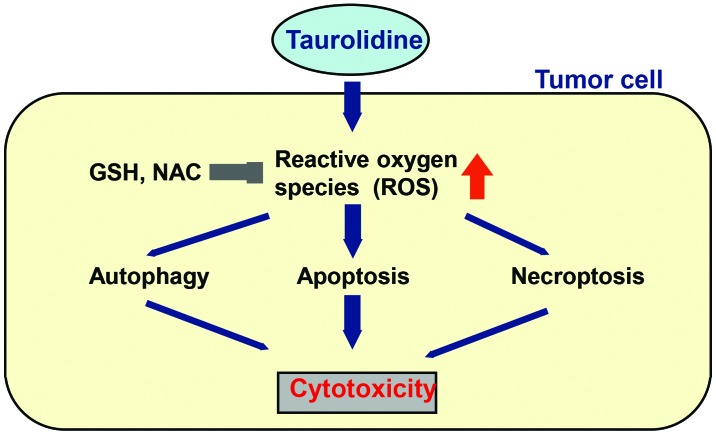
Figure 1.
The proposed antineoplastic action of Taurolidine. By increasing ROS, Taurolidine induces cytotoxicity in tumor cells largely by induction of apoptosis, but also autophagy and necroptosis. The degree to which these processes are involved may vary with the type of tumor cell. Reducing agents such as N-acetylcysteine (NAC) or glutathione (GSH) inhibit cytotoxicity, which supports the mechanism of redox-directed antineoplastic activity.