Figure 2.
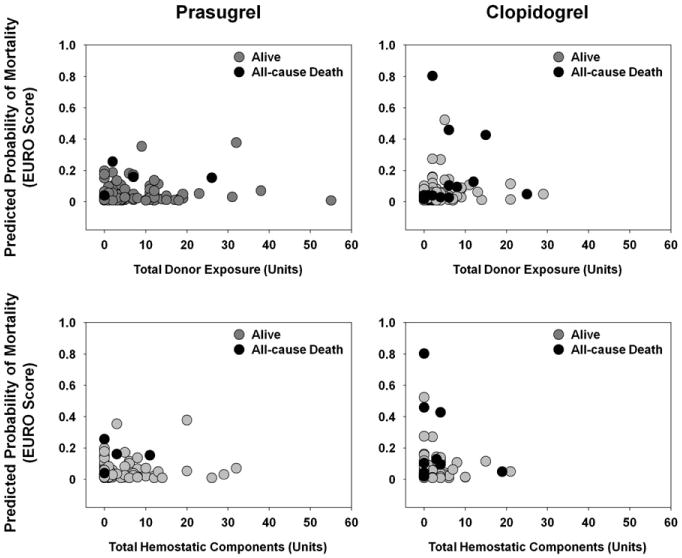
Predicted probability of mortality as function of total donor exposure and function of total hemostatic components. In analyses adjusted for predicted risk of mortality (using European System for Cardiac Operative Risk Evaluation Score [euroSCORE]), increased mortality risk (all-cause death within 30 days after coronary artery bypass grafting [CABG]) was not associated with total donor exposure (odds ratio, 1.06; 95% confidence interval, 0.98-1.14; P = .15; logistic regression analysis) nor total hemostatic components (odds ratio, 1.05; 95% confidence interval, 0.94-1.17; P = .40; logistic regression analysis). Prasugrel was independently associated with reduction in mortality (prasugrel, 1.2%; clopidogrel, 6.9%; P = .022). Total donor exposure included red blood cells, platelets, cryoprecipitate, and plasma; total hemostatic components included platelets, cryoprecipitate, and plasma.
