Figure 4. Model for symbiotic and mutagenic plasmid-driven evolution of rhizobia.
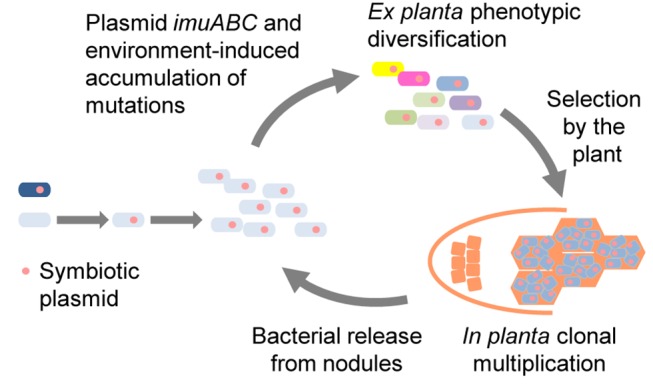
Following horizontal transfer of a symbiotic plasmid to a soil bacterium, the recipient genome accumulates environment-induced mutations that lead to phenotypic diversification. The most beneficial variants are selected by the plant and clonally multiply within nodules before being released. Rounds of ex planta phenotypic diversification/plant selection/clonal multiplication may have driven the adaptation process in natura.
