Fig. 1.
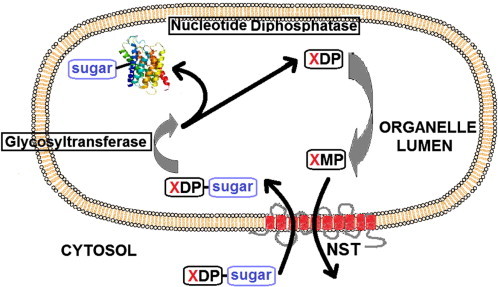
The general transport mechanism of NSTs. The XDP-sugar (nucleotide sugar donor) enters the lumen of the organelle in exchange for the corresponding nucleoside monophosphate (XMP). After entering the lumen the sugar is transferred to either a protein or lipid in a reaction catalysed by glycosyltransferases. The diphosphate nucleotide (XDP) is then acted upon by a membrane-bound nucleotide diphosphatase [37] producing the XMP that is subsequently exported [38]. In some cases where the nucleotide sugar donor is a monophosphate, the dephosphorylation reaction performed by the diphosphatase is not required.
