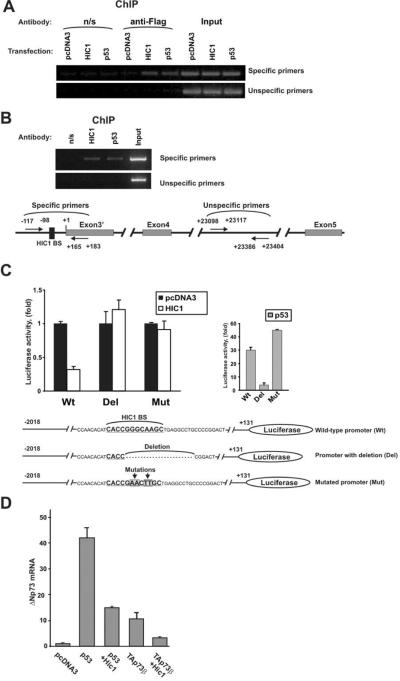
Figure 4. HIC1 protein binds to the ΔNp73 promoter.
A. Binding of HIC1 to the native ΔNp73 promoter. SNU1 cells were transfected with the indicated Flag-tagged plasmids. HIC1 binding was analyzed by ChIP with anti-Flag antibody (M2, Sigma, St Louis, MO) using the ChIP Assay Kit from Upstate Biotechnology (Lake Placid, NY). B. Endogenous HIC1 protein binds to the ΔNp73 promoter. ChIP analysis was performed with HIC1-specific antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA) in SNU1 cells. As negative and positive controls precipitations with non-specific rabbit IgG (Jackson ImmunoResearch) and p53-specific antibody (DO1, Calbiochem, La Jolla, CA) were performed, respectively. Bottom panel: positions of ChIP primers. Sequences of primers are shown in Supplementary Table 4. C. Deletion or mutation of the HIC1 BS attenuates the inhibitory function of HIC1 at the ΔNp73 promoter. MKN75 gastric cancer cells were transfected with the indicated luciferase reporters and HIC1 activity was then analyzed using reporter assay. Bottom panel shows sequences of ΔNp73 luciferase reporters. Mutated ΔNp73 reporter was generated by site-directed mutagenesis using the site-directed mutagenesis kit (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA). MKN75 were maintained in RPMI media (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) supplemented with 10% FBS. ΔNp73 luciferase reporter was kindly provided by Dr. Melino. D. HIC1 inhibits expression of ΔNp73 mRNA induced by p53 and TAp73. MKN28 gastric epithelial cells were maintained in RPMI medium supplemented with 10% FBS. Cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids and expression of ΔNp73 mRNA was analyzed using qPCR as described previously (Vilgelm et al., 2008b).