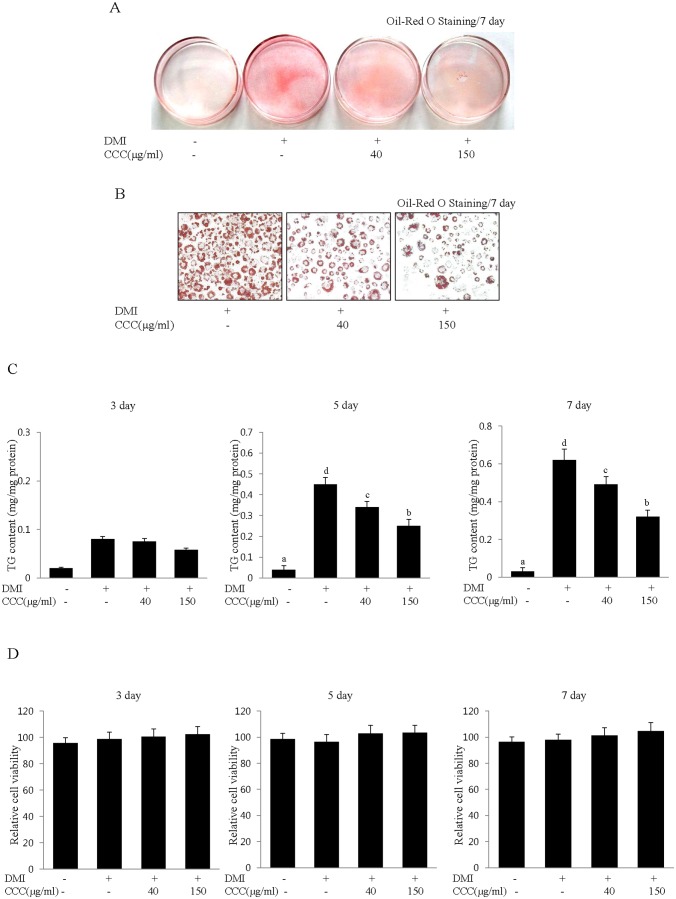
Figure 1. CCC inhibits lipid accumulation during the differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes.
(A) Insulin-induced differentiation of 3T3-L1 adipocytes was repressed by CCC. Confluent 3T3-L1 preadipocytes were differentiated into adipocytes in DMI medium containing different concentrations (0, 40, or 150 µg/ml) of CCC for 7 days (from day 0 to 7). (A) The insulin-induced differentiation of 3T3-L1 adipocytes was repressed by CCC treatment. Oil-Red O staining was performed on day 7 after the induction of differentiation. DMI: Adipogenic differentiation medium (0.5 mM 3-IBMX, 100 µM indomethacin, 0.25 µM dexamethasone and 167 nM insulin). CCC: Coprinus comatus cap extract. (B) Microscopic observations of the Oil-Red O staining showed a gradual reduction in the lipid content of the 3T3-L1 adipocytes after CCC treatment. (C) Effects of CCC extract on intracellular triglyceride accumulation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. The triglyceride content was significantly reduced by CCC treatment on days 3, 5, and 7 after the induction of differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells. The data shown are representative of at least three independent experiments. The values are presented as the mean ± SD. The bars with different letters are significantly different (*p<0.05) as determined by Duncan's multiple range test. (D) Effects of CCC on cell cytotoxicity in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. The cells were incubated for 7 days with various concentrations (0, 40, or 150 µg/ml) of CCC after the induction of differentiation. Cell viability was measured on days 3, 5, and 7 using an MTT assay. The results were confirmed by three independent experiments, which were each conducted in triplicate. The data are presented as the mean ± SD.