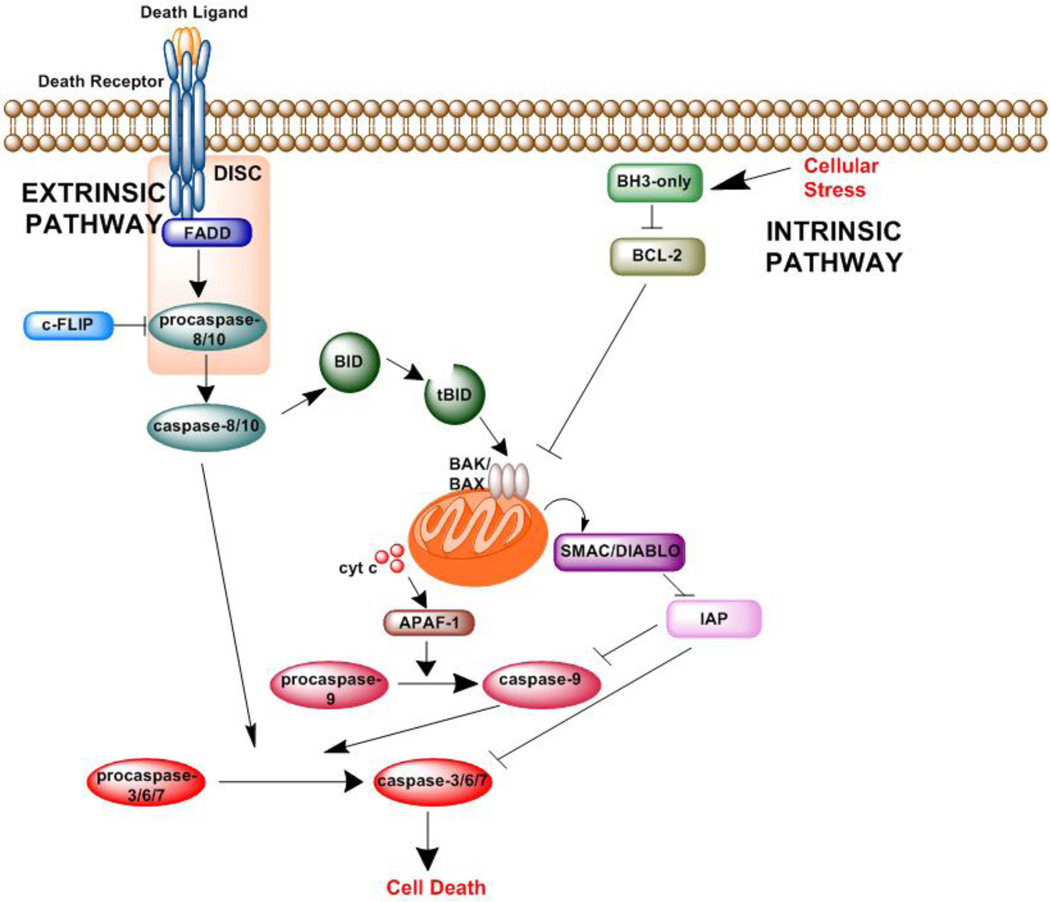
Figure 1. The apoptosis pathway.
There are two apoptosis pathways, intrinsic and extrinsic. The intrinsic pathway is activated by cellular stress. When activated, the BH3-only proteins inhibit antiapoptotic BCL-2 proteins and induce BAK/BAX oligomerization and permeabilization of the mitochondria and release of cytochrome c and SMAC/DIABLO. Cytochrome c forms a complex with caspase-9 and APAF-1, leading to activation of caspase-9. Caspase-9 activates the executioner caspases (caspase-3, −6, and −7) and induces cell death. The extrinsic pathway is activated by death signals mediated by death ligands. The death ligand activates the death receptor, which forms a complex called the death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) and sends a signal to activate caspase-8 and −10. Caspase-8 and −10 activate caspase-3. In some cells, the extrinsic pathway crosstalks with the intrinsic pathway through caspase-8–mediated truncation of BID to tBID. tBID activates BAK/BAX oligomerization and induces apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway.