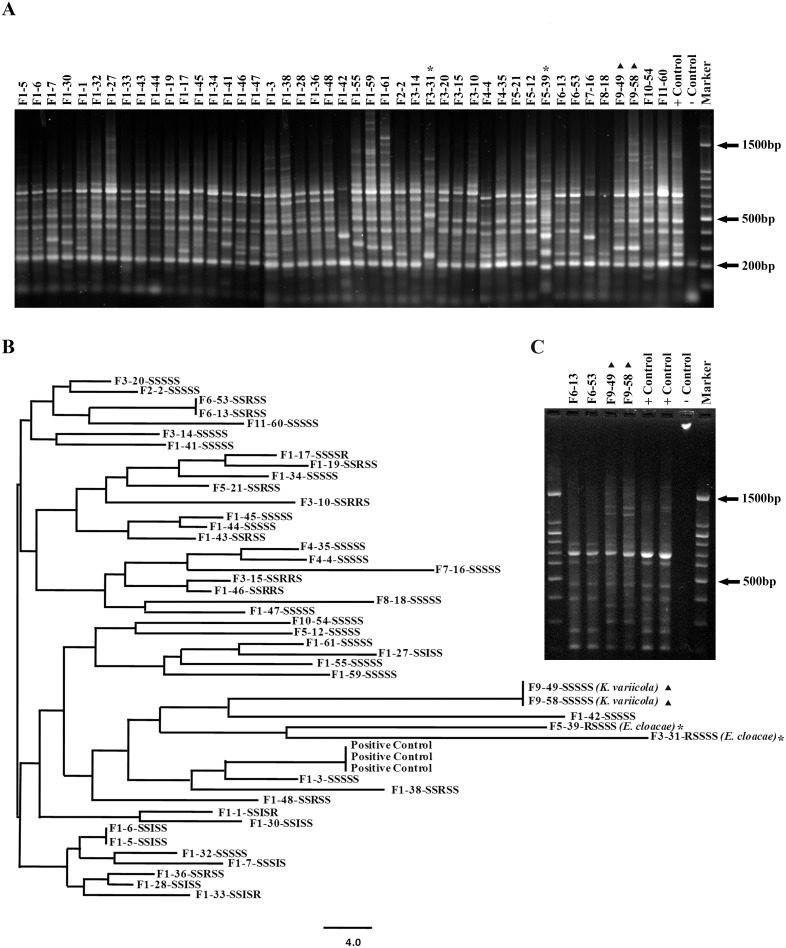
Figure 1. Molecular epidemiology of CM associated coliform bacteria isolated over a one year period from 11 dairy herds in Newfoundland.
(A) Results from RAPD analysis employing 1.5% agarose gels to separate PCR products. Chromosomal DNA from a laboratory strain (K. pneumoniae ATCC 15380) was included as the positive control and sterile water functioned as negative control in the PCR assays. A 100 bp ladder (Cat No. DM001-R500, GeneDirex, USA) was used as the molecular weight marker (B) Dendrogram based on RAPD results showing relatedness between strains subjected to analysis in the current study. The dendrogram was generated by the neighbor joining method with the PyElph software. (A, B and C) The isolates were assigned labels based on the farm or origin (F1 to F11) followed by a number to identify the infected animal. The isolates determined to be E. cloacae (*) and K. variicola (▴) are also indicated. (B) The results from antibiotic susceptibility testing are also shown next to each isolate. S: sensitive, I: intermediate and R: resistant designations are assigned based on established break points. The S/I/R designations for each drug are in the following order: cephalothin, ceftiofur, streptomycin, tetracycline and trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole, respectively. The isolates identified as K. variicola and E. cloacae on further analysis are also indicated. (C) Re-analysis of strains by RAPD PCR to verify the accuracy of the assay and to confirm identities. PCR products generated independently for the second time using DNA from identical strains along with the positive control were reanalyzed, which confirmed results shown in A.