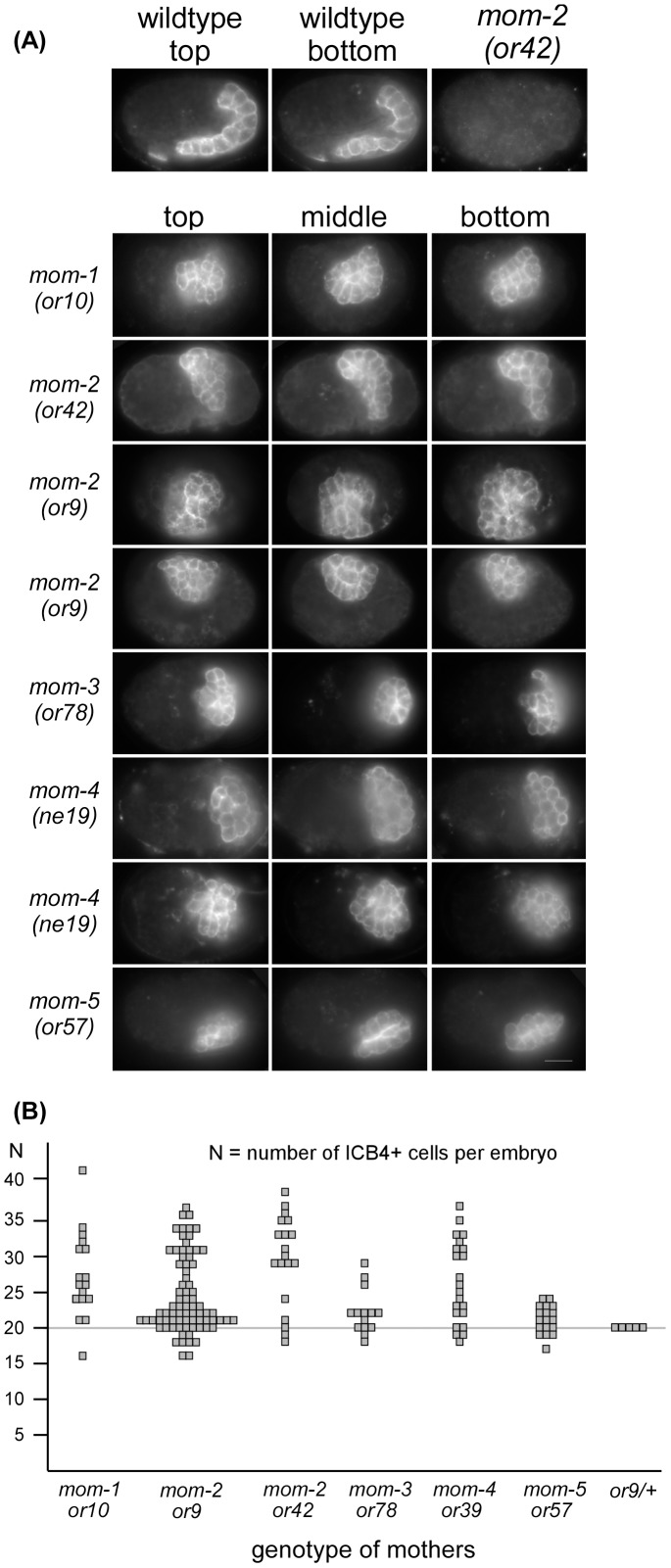
Figure 6. Intestine development in Wnt/MAPK mutant embryos.
(A) Differentiated intestinal cells stained with ICB4 antibody. The first two panels of the top row show a wildtype embryo imaged at two different focal planes. The third panel is a representative mom-2(or42) mutant embryo that did not develop intestinal cells. The following rows are examples of embryos with the indicated mutation that did develop ICB4-positive cells, imaged at three different focal planes (top, middle, and bottom). Note that in all the mutant embryos the number of ICB4-positive cells exceeds 20. Furthermore, the intestine is not elongated as in the wildtype, and instead appears as a clump of small cells. (B) Summary of ICB4-positive cell counts per embryo for the indicated Wnt and MAPK mutants. Note that the number spread from the wildtype number (20) is much restricted for the Wnt frizzled receptor mutant, mom-5(or57), versus the other mutants, and that mom-2(or9/+) heterozygous embryos develop the wildtype number of intestinal cells (indicating that a single wildtype copy of mom-2 is sufficient to determine E lineage cell-division number).