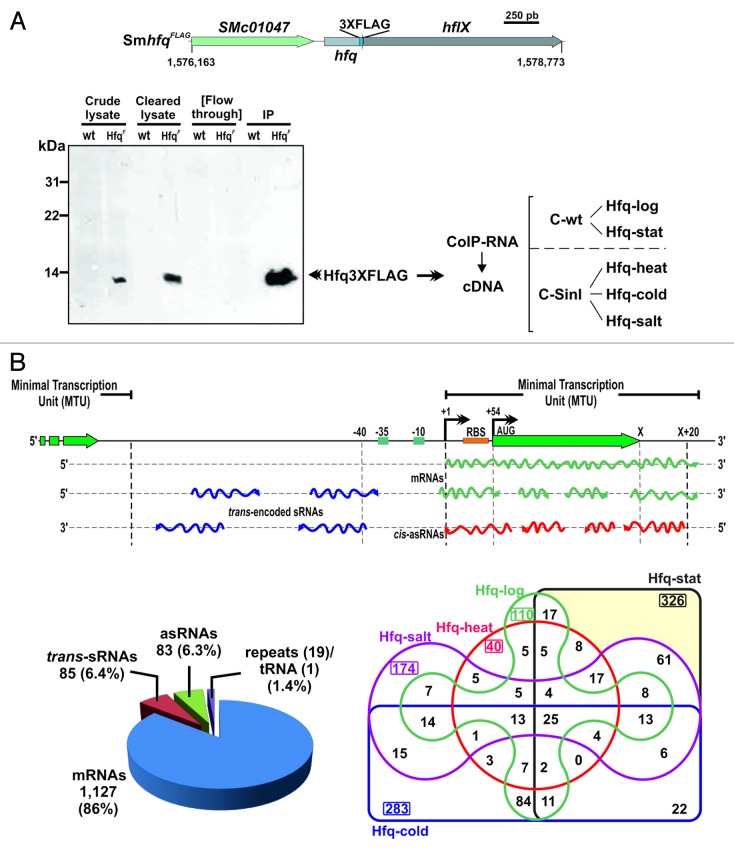
Figure 1. Identification of Hfq-binding transcripts in S. meliloti. (A) Experimental setup. Chromosomal hfq region in S. meliloti with indication of tagging in the Sm2B3001 derivative strain SmhfqFLAG (coordinates according to the annotation of the reference S. meliloti 1021 genome). Below is a western blot probed with Anti-FLAG M2® antibodies showing the specific recognition and recovery of the FLAG-tagged Hfq in the different protein fractions from TY exponential cultures of SmhfqFLAG during CoIP. As a control the same fractions from the wild-type (wt) strain Sm2B3001 were similarly probed. CoIP–RNA was recovered from Hfq–RNA complexes (IP fraction) derived from Sm2B3001, SmpWsinIFLAG, and SmhfqFLAG strains grown to exponential and stationary phases in TY and upon cold, heat, and salt shocks. cDNA libraries for sequencing were generated from control and Hfq CoIP–RNA samples (see text for details). (B) Classification of Hfq-bound transcripts. A schematic of the different types of Hfq RNA species according to the MTU model described in Materials and Methods is shown on the upper panel. Lower panels show the number of Hfq-bound RNAs in both each category (left circle diagram) and cDNA library (right Venn diagram).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.