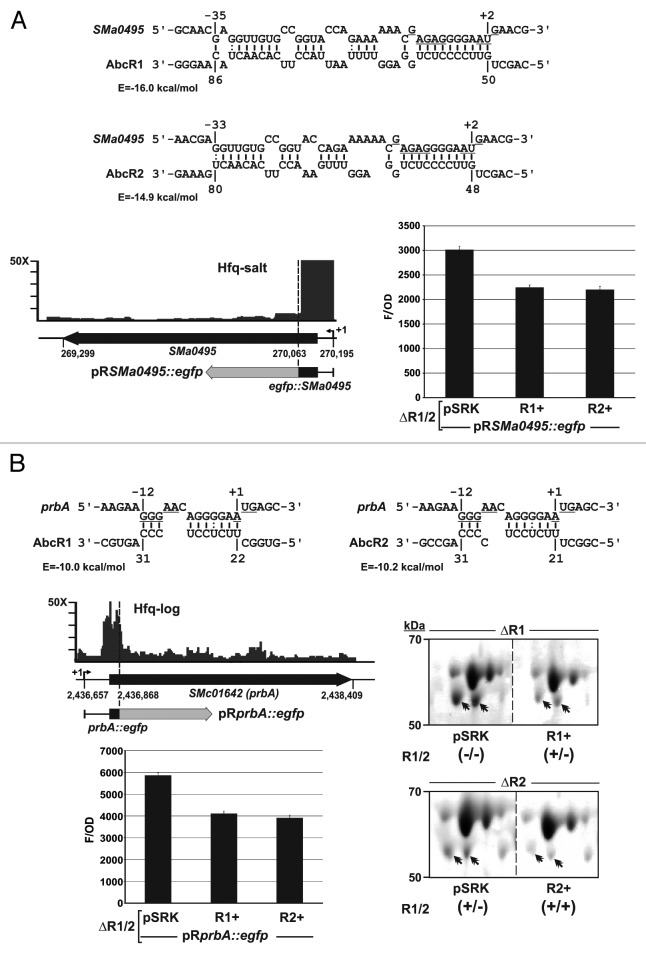
Figure 6. Targeting of the SMa0495 (A) and prbA (B) mRNAs by the AbcR1 and AbcR2 sRNAs. IntaRNA predicted duplexes are shown, with the RBS and AUG start codons of the SMa0495 and prbA mRNAs underlined. In these diagrams, numberings denote positions relative to the AUG start codon of the mRNA and the TSS of AbcR1 and AbcR2. The predicted minimum hybridization energy (E) is indicated in each case. The IGB diagrams show the fold enrichment (vertical axis) of these mRNAs in the indicated Hfq CoIP–RNA library. Schematics of the reporter fusions cloned in plasmid pR-EGFP are shown below the genomic information of each mRNA. The histograms show the fluorescence of the reporter S. meliloti double deletion mutant (∆R1/2) co-transformed with the target fusions and plasmids pSRK (empty control vector), pSRK-R1 (R1+), or pSRK-R2 (R2+). Values reported are means and standard deviation of 48 fluorescence measurements, i.e., four determinations in three independent exponential cultures of four double transconjugants representing each plasmid combination. Fluorescence values were normalized to culture OD600 (F/OD). Background fluorescence from strains harboring pSRK and the empty pR-EGFP plasmid instead of the target fusions was subtracted from the fluorescence of target fusions. Relevant subsections of 2D-PAGE gels revealing downregulation of the periplasmic protein PrbA (double arrowhead) by both AbcR1 and AbcR2 sRNAs are also shown. Periplasmic protein extracts were obtained from exponential cultures of S. meliloti single mutants ∆R1 and ∆R2 carrying pSRK or either pSRK-R1 (R1+) or pSRK-R2 (R2+) as indicated. Expression/absence (+/−) of AbcR1 and AbcR2 (R1/2) in each strain is indicated in brackets. Note that AbcR1 is highly expressed from the chromosome whereas AbcR2 is almost absence in exponentially growing bacteria.42

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.