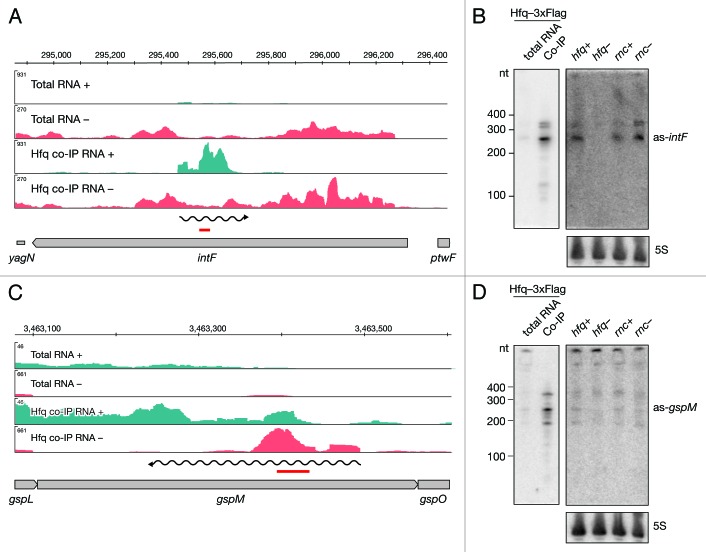
Figure 3. Identification and verification of antisense RNAs binding to Hfq. Deep sequencing results of as-intF and as-gspM (A and C) represented as averaged coverage maps of 3xFlag- and HA total RNAs and 3xFlag- and HA-co-immunoprecipitated RNAs (Hfq co-IP). The genomic strands are shown in blue (+) and red (-). Note that scales for the + and – strand differ. The genomic location is depicted on top and the genomic context is depicted below. The red bar indicates the position of the oligonucleotide probe that was used in the corresponding Northern. The wavy line represents the predicted position of the novel RNA. Northern blot analyses of as-intF and as-gspM (B and D). Hfq-3xFlag total RNA and RNA co-immunoprecipitated with Hfq-3xFlag (left panel) and total RNA isolated from hfq deletion strain (hfq-), corresponding isogenic wild type (hfq+), RNase III mutant (rnc-) and corresponding isogenic wild-type cells (rnc+) (right panel) were fractionated on a denaturing 8% polyacrylamide gel, electro-blotted onto a nylon membrane and hybridized with radioactively labeled oligonucleotide. Note that different amounts of RNA were loaded; 20 μg total RNA and 1 μg co-IP RNA. Ladder sizes in nt are indicated. 5S RNA was used as a loading control. At least two independent experiments were performed and representative data are shown.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.