Figure 3.
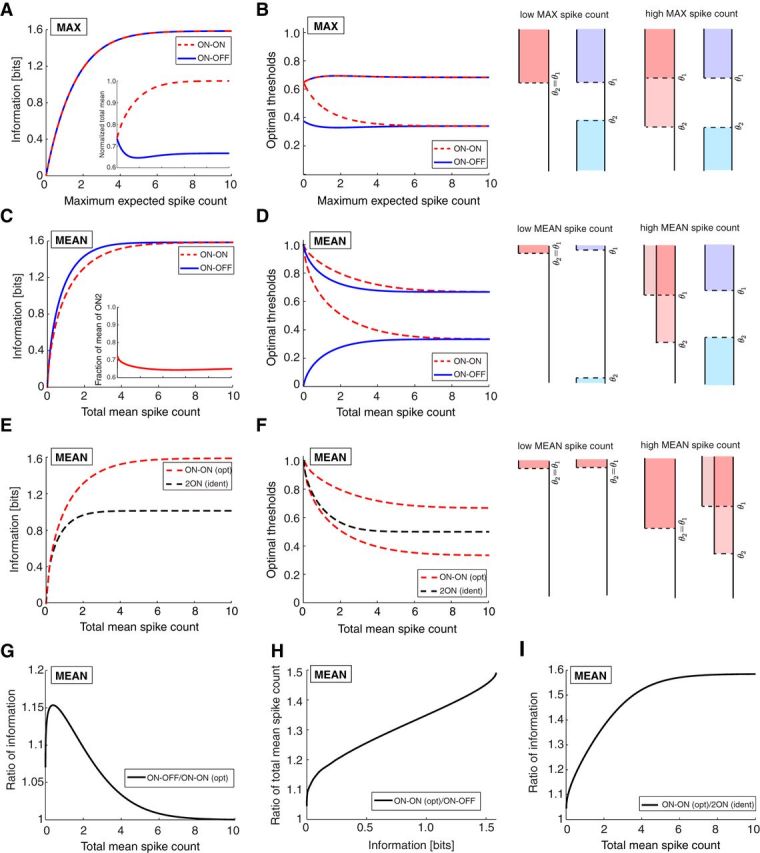
Mutual information with binary neurons and Poisson output noise. A, The mutual information for an ON–OFF and an ON–ON system is identical when constraining the maximum expected spike count, Nmax. Inset, The ON–ON system uses more spikes to convey the same information. The total mean is normalized by Nmax. B, The thresholds of the response functions for the optimal ON–OFF and ON–ON systems when constraining Nmax. Right, Optimal response functions in the limits of low and high Nmax. C, The ON–OFF system transmits more information than the ON–ON system when the total mean spike count is constrained. Inset, the fraction of total mean spike count assigned to the ON cell with the smaller threshold. D, The thresholds of the response functions for the optimal ON–OFF and ON–ON systems when constraining the total mean spike count. Right, Optimal response functions in the limits of low and high mean spike count (compare with B). E, The optimal ON–ON system transmits more information than a system of identical ON cells. F, The thresholds of the response functions for the optimal ON–ON and identical 2ON systems as a function of the total mean spike count. G, The ratio of mutual information transmitted by the optimal ON–OFF versus ON–ON systems in C. H, The ratio of mean spike counts required to convey the same information by the ON–ON versus ON–OFF systems. I, The ratio of mutual information from the optimal ON–ON versus identical 2ON systems in E.
