Abstract
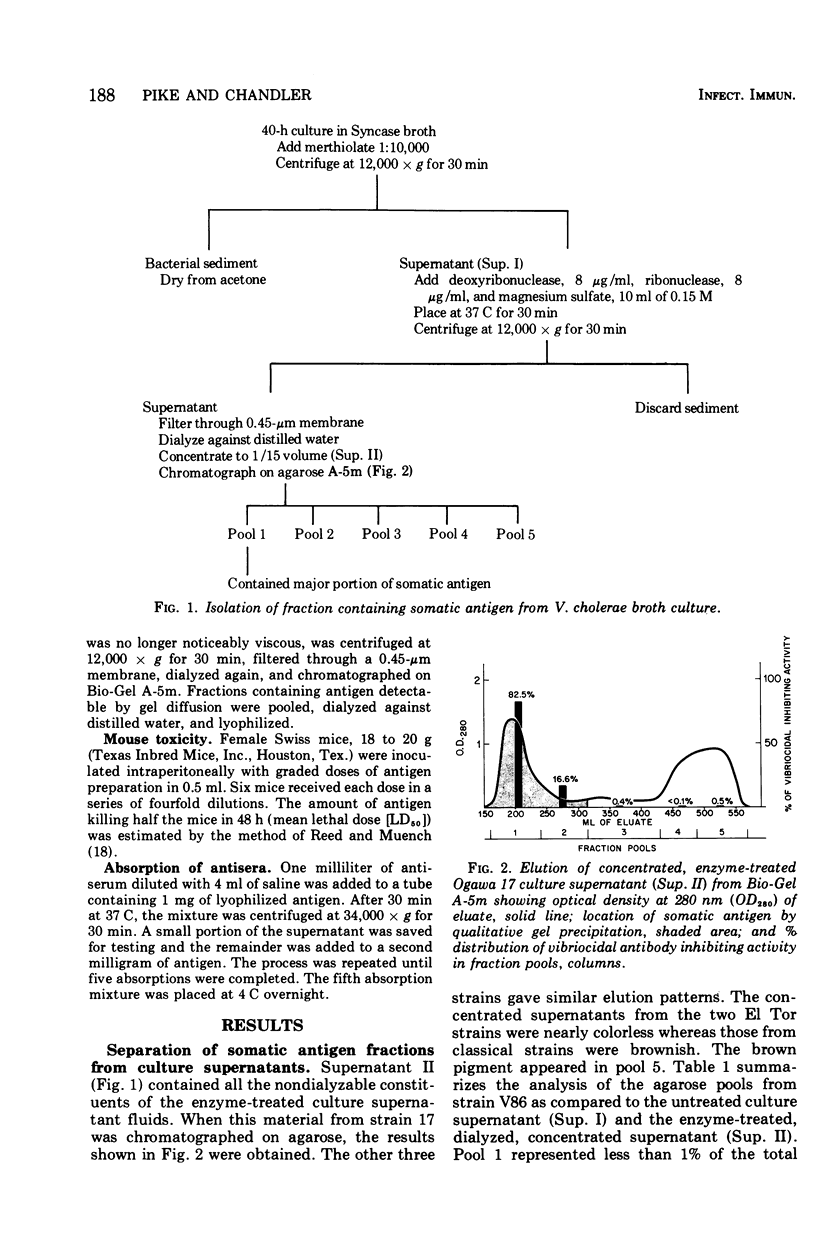
The supernatant fluids from cultures of Vibrio cholerae grown for 40 h in an dialyzable medium were dialyzed, concentrated, and fractionated on agarose columns. The fractions containing most of the antigen which inhibited the vibriocidal activity of homologous antiserum were pooled, dialyzed, and concentrated to provide material with about 100 times the specific activity of the original culture supernatant. This material, containing 12 to 20% protein, 11 to 19% carbohydrate, and about 16% unbound lipid, had a mean lethal dose for mice of about 500 mug. This partially purified antigen absorbed all the vibriocidal antibody from homologous antiserum against live cultures and produced a single line of precipitation in gel diffusion tests with the same antiserum.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chatterjee S. N., Das J. Electron microscopic observations on the excretion of cell-wall material by Vibrio cholerae. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Oct;49(1):1–11. doi: 10.1099/00221287-49-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crutchley M. J., Marsh D. G., Cameron J. Biological studies on free endotoxin and a non-toxic material from culture supernatant fluids of Escherichia coli 078K80. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Mar;50(3):413–420. doi: 10.1099/00221287-50-3-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crutchley M. J., Marsh D. G., Cameron J. Free Endotoxin. Nature. 1967 Jun 3;214(5092):1052–1052. doi: 10.1038/2141052a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINKELSTEIN R. A., NORRIS H. T., DUTTA N. K. PATHOGENESIS EXPERIMENTAL CHOLERA IN INFANT RABBITS. I. OBSERVATIONS ON THE INTRAINTESTINAL INFECTION AND EXPERIMENTAL CHOLERA PRODUCED WITH CELL-FREE PRODUCTS. J Infect Dis. 1964 Jun;114:203–216. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.3.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Atthasampunna P., Chulasamaya M., Charunmethee P. Pathogenesis of experimental cholera: biologic ativities of purified procholeragen A. J Immunol. 1966 Mar;96(3):440–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lönnroth I., Ouchterlony O. Immunochemical Studies of Two Cholera Toxin-Containing Standard Culture Filtrate Preparations of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1971 Jun;3(6):747–755. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.6.747-755.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUR J., SHRIVASTAV J. B. IMMUNOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON VIBRIO POLYSACCHARIDES. Indian J Med Res. 1964 Aug;52:809–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy J. R., Richardson S. H. Fine structure of Vibrio cholerae during toxin production. J Bacteriol. 1969 Dec;100(3):1393–1401. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.3.1393-1401.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Cullen J., Work E. An extracellular lipopolysaccharide-phospholipid-protein complex produced by Escherichia coli grown under lysine-limiting conditions. Biochem J. 1967 Apr;103(1):192–201. doi: 10.1042/bj1030192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Vesk M., Work E. Relation between excreted lipopolysaccharide complexes and surface structures of a lysine-limited culture of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1206–1217. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1206-1217.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOWOTNY A. M., THOMAS S., DURON O. S., NOWOTNY A. Relation of structure to function in bacterial O antigens. I. Isolation methods. J Bacteriol. 1963 Feb;85:418–426. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.2.418-426.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neoh S. H., Rowley D. The antigens of Vibrio cholerae involved in the vibriocidal action of antibody and complement. J Infect Dis. 1970 May;121(5):505–513. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.5.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike R. M., Chandler C. H. Serological Properties of gammaG and gammaM Antibodies to the Somatic Antigen of Vibrio cholerae During the Course of Immunization of Rabbits. Infect Immun. 1971 Jun;3(6):803–809. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.6.803-809.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike R. M., Chandler C. H. The spontaneous release of somatic antigen from Vibrio cholerae. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Mar;81(1):59–67. doi: 10.1099/00221287-81-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]