Figure 1.
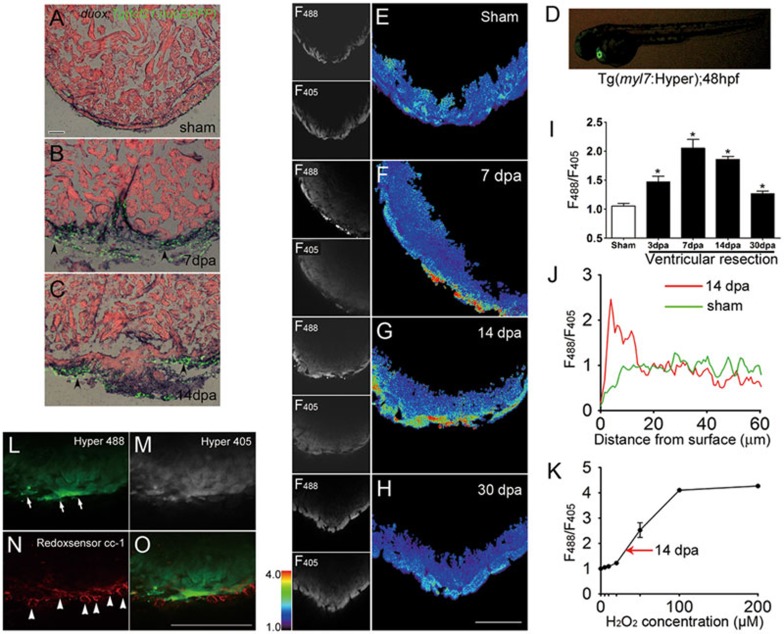
Epicardial Duox-generated H2O2 associated with myocardial regeneration. (A-C) After imaging of Tg(tcf21:nucEGFP), we performed RNA in situ hybridization with duox probes on 10-μm cryosections of Tg(tcf21:nucEGFP) hearts at sham, 7 and 14 dpa. Note the induced expression of duox and its colocalization with epicardial reporter Tg(tcf21:nucEGFP) in injured areas (arrowheads) at 7 and 14 dpa (B, C) while little staining at sham (A). Scale bar for A-C, 50 μm. (D) Cardiac-specific expression of Hyper in a zebrafish embryo. Hyper was restricted in the Tg(myl7:Hyper) transgenic heart at 48 hpf. (E-H) Ex vivo Hyper heart images from sham control (E), 7 dpa (F), 14 dpa (G) and 30 dpa (H). Spatially resolved H2O2 image, indexed by the ratio between the F488 and F405 images of Hyper (left panels), is presented in pseudocolor. (I) Ratiometric Hyper signals (F488/F405) averaged over the regenerative zone of injured heart during the first month of regeneration after resection. n = 3. (J) Representative transmural spatial profiles of the Hyper signal at 14 dpa (red line) and sham (green line) hearts. (K) Ex vivo calibration of Hyper F488/F405 ratio as a function of ambient H2O2 concentration. n = 3. Arrow denotes the average F488/F405 ratio seen in regenerative zones at 14 dpa. (L-O) Redox signal showing greater epicardial and myocardial oxidization during regeneration. A 14 dpa Tg(myl7:hyper) heart was labeled with Redox sensor cc-1. Images show Hyper signals at 488 (L) and 405 nm (M), and Redox sensor cc-1 signals at 555 nm excitation (N), and the merging of L and N (O). Note that the Redox sensor cc-1 signal (arrowheads), indicative of intracellular oxidization, was most conspicuous in epicardial cells lacking Hyper expression, and also overlapped with the Hyper signal (arrows) in adjacent myocardium. Scale bars, 100 μm.