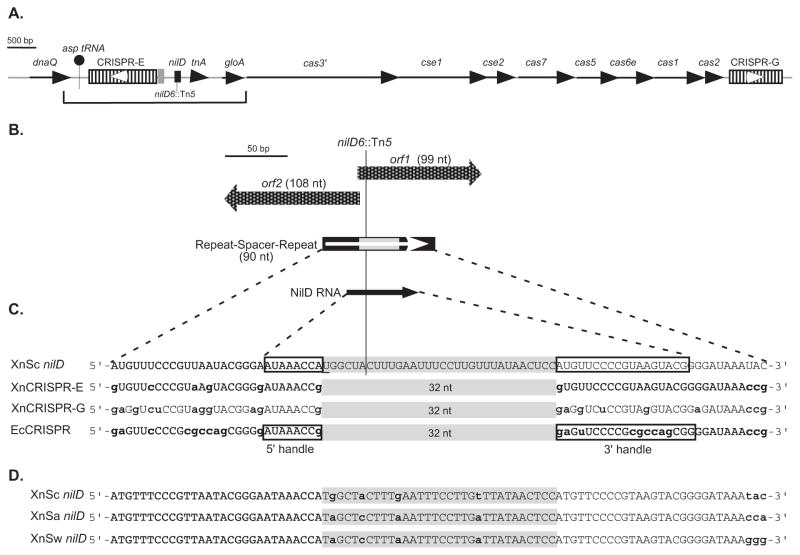
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the nilD CRISPR locus.
A. Schematic diagram of the X. nematophila genomic regions containing CRISPR loci, cas/cse genes, and nilD. The bracket indicates the 3240-bp region previously sequenced in the HGB081 (XnSc 081) strain background (AY077466) (Heungens et al., 2002), which is identical in the sequenced ATCC 19061 (HGB800/XnSc 800) genome (NC_014228.1). Line arrows represent open reading frames, with gene names indicated above each. CRISPR loci are represented by hatched rectangles and are named CRISPR-E and CRISPR-G according to their position on the X. nematophila genome, with nilD, shown as a black rectangle, considered CRISPR-F. The location of the nilD6::Tn5 transposon insertion within nilD is indicated. The gray shaded box represents the 135-bp leader sequence of CRISPR-E. White arrowheads indicate the predicted orientations of CRISPR-E and -G transcription, based on comparison to E. coli CRISPR transcription.
B. Detail of the nilD locus, showing the two small overlapping open reading frames (orf1 and orf2) represented by checkered block arrows. The positions of nilD locus repeats and spacer are indicated by black and gray rectangles, respectively. The white arrow indicates the predicted orientation of transcription based on comparison to E. coli CRISPR transcription. The black arrow represents the position of the small RNA transcript encoded by the nilD locus. The position of the nilD6::Tn5 insertion site is indicated by a line.
C. Sequence of NilD RNA aligned with CRISPR small RNAs predicted to be encoded by X. nematophila (XnCRISPR-E and -G) and CRISPR RNAs expressed in E. coli (EcCRISPR). Spacer regions are shaded in gray. Lower case, bold nucleotides indicate those that differ from NilD RNA. The 5′ and 3′ handles as described by Brouns et al. (2009), and experimentally determined for NilD RNA are boxed. The underlined “U” in the nilD spacer sequence is necessary for colonization (Heungens et al., 2002).
D. Alignment of nilD locus repeat-spacer-repeat sequences of X. nematophila (carpocapsae) (XnSc nilD), X. nematophila (anatoliense) (XnSa nilD), and X. nematophila (websteri) (XnSw nilD). Lower case bold letters indicate nucleotides that differ among the three sequences.