Figure 2.
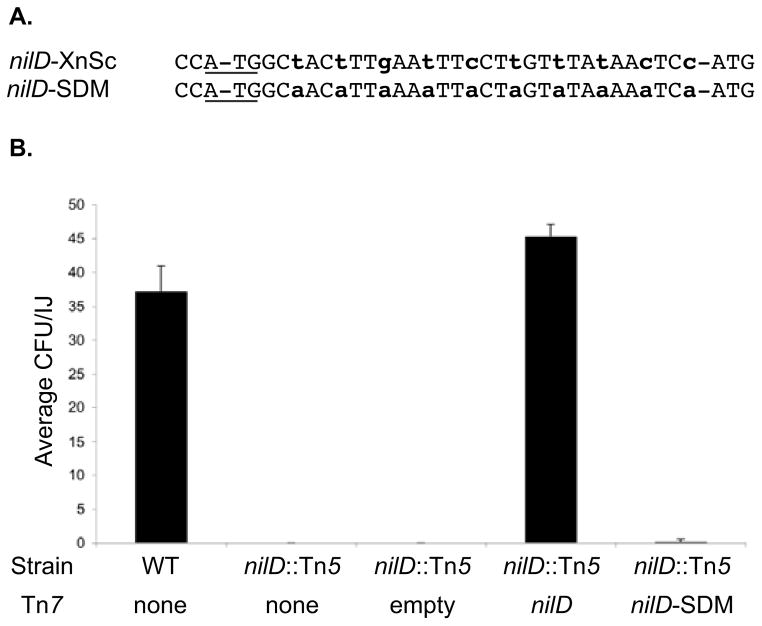
Wild type, but not mutant nilD provided in trans complements the colonization defect of the nilD6::Tn5 mutant
A. Alignment of the spacer sequences of X. nematophila (from S. carpocapsae) wild type nilD (nilD-XnSc) and the mutated allele (nilD-SDM).
B. XnSc 081, XnSc 081 nilD::Tn5, and complemented strains were co-cultivated with axenic S. carpocapsae nematodes. The average colony forming units (CFU) colonizing the resulting progeny infective juveniles was measured by sonication and dilution plating.