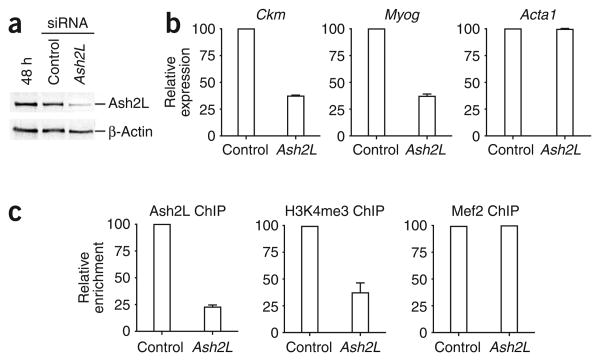
Figure 6.
Knockdown of Ash2L in C2C12 cells leads to reduced transcription of the Myog and Ckm genes. (a) Whole-cell extracts prepared from differentiating C2C12 cells after indicated siRNA treatments were subjected to western blotting analysis with anti-Ash2L or anti–β-actin. (b) Knockdown of Ash2L leads to decreased expression of muscle-specific genes. RNA was isolated from differentiating C2C12 cells (48 h) transfected with siRNA targeting Ash2L or with untargeted control siRNA. RNA was extracted, reverse-transcribed and subjected to qPCR analysis with primers recognizing the genes indicated. Expression is reported relative to the control 18S RNA signal. Average values of triplicate qRT-PCR reactions are shown; error bars represent s.d. Each experiment was performed at least twice with independently isolated RNA. (c) C2C12 cells were transfected with siRNA targeting Ash2L or with untargeted control siRNA. Transfected cells were then differentiated for 48 h and analyzed by ChIP for enrichment of Ash2L, H3K4me3 and Mef2 at the Myog promoter. After deproteination, immunopurified DNA was quantified by qRT-PCR with hydrolysis probes. Average values of duplicate qPCR reactions are shown; error bars represent s.d. Each experiment was performed at least twice with independent chromatin samples and yielded similar results both times.