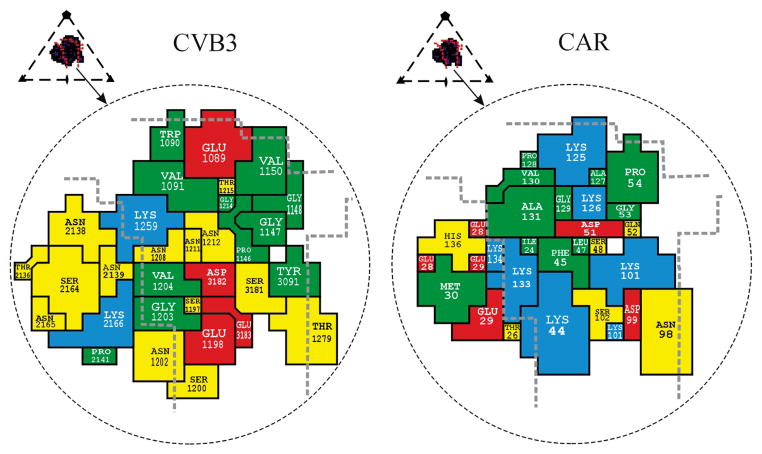
Fig. 4.
Footprint of domain D1 onto the CVB3 surface (left) and footprint of CVB3 onto CAR (right). Inset shows the icosahedral asymmetric unit of the virus, the rough boundaries of the canyon (red lines) and the perimeter of the receptor footprint. The amino acids forming the interface are colored as follows: red for acidic residues, blue for basic residues, yellow for polar residues and green for hydrophobic residues. Thick dashed gray lines highlight the canyon boundaries. The CAR amino acids are numbered in accordance with the system used by Bewley et al.21 (PDB 1KAC); these sequence numbers are greater by two than those used by van Raaij et al.24 (PDB 1F5W).