Figure 5.
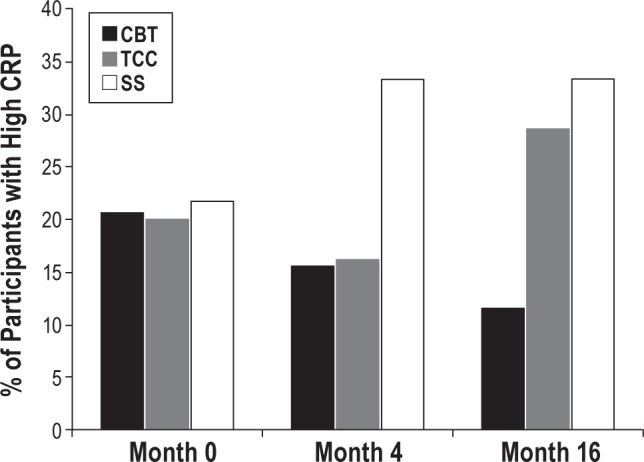
Percentage of participants with high C-reactive protein (CRP) at baseline, 4 months, and 16 months in the CBT, TCC, and SS treatment groups. High CRP was defined by levels in excess of 3.0 mg/L. High CRP was less likely to be found in the CBT participants as compared to SS (χ2(1) = 4.0, P = 0.04). As compared to SS, CBT was associated with a reduced risk of having high CRP at 4 months (odds ratio [OR], 0.37 [95% CI, 0.11–1.18]; P = 0.08) and at 16 months (OR, 0.26 [CI, 0.07–0.97]; P < 0.05). As compared to SS, TCC was not associated with reduced risk of high CRP at 4 months (OR, 0.39 [CI, 0.11–1.3] P = 0.10), or at 16 months (OR, 0.8; [CI, 0.25–2.5] P = 0.47). In SS, change in percentage with high CRP from baseline to month 16 was not significant (P > 0.30). CBT, cognitive behavioral therapy; TCC, Tai Chi Chih; SS, sleep seminar.
