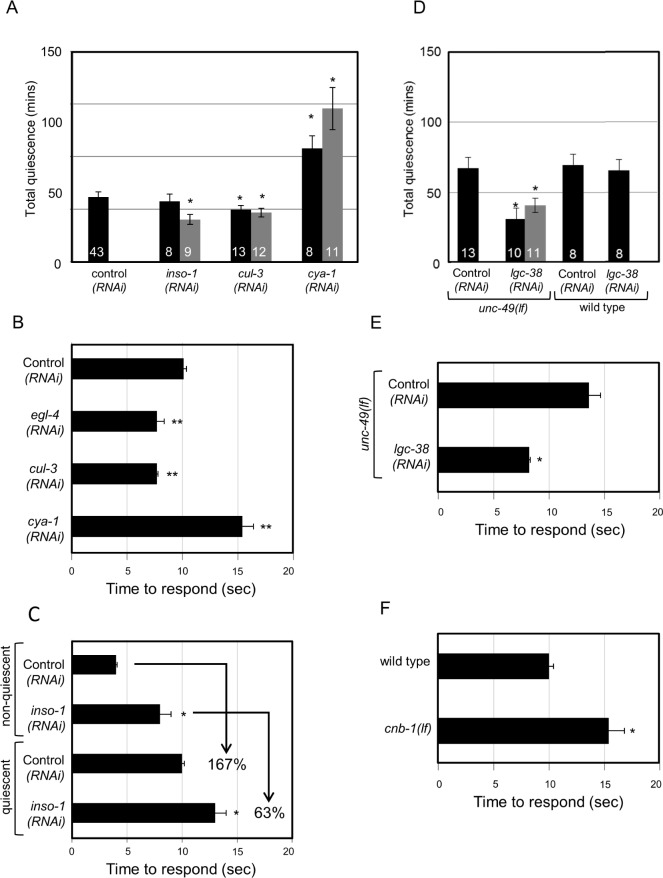
Figure 2.
Lethargus quiescence and altered arousal during sleep requires the function of conserved genes. For RNA interference (RNAi) feeding experiments, HA2158 animals expressing the SID-1 double- stranded RNA channel in neurons were used.77 Total quiescence during L4-to-adult lethargus reported in min. Arousal thresholds were determined by measuring the time to respond to 60% dilute 1-octanol. Response time is reported in sec. Error bars represent standard error of the mean (s.e.m.). Gray and black bars represent independent clones in A and D. Numbers inside the bar indicate sample size. For each gene examined, independent sets of control animals were tested in parallel and these were used to determine significance by Student t test. P < 0.05* < 0.01** and < 0.001*** versus control (RNAi), unc-49(lf), or wild-type. Results were grouped and controls were pooled for concise presentation. (A) RNAi knockdown using two independent clones of insomniac (inso-1) and cullin-3 (cul-3) decreased total quiescence with one exception. See Methods for a possible off-target gene for inso-1(RNAi). RNAi knockdown of cyclin A (cya-1) increased total quiescence. (B) RNAi knockdown of egl-4 and cul-3 in sensitized HA2158 animals lowered arousal thresholds during quiescence in comparison with their respective controls. RNAi knockdown of cya-1 increased arousal thresholds. (C) Nonquiescent inso-1(RNAi) animals were mildly 1-octanol sensing defective. Quiescent wild-type animals' response time to dilute 1-octanol increased by 167 ± 11%. However, inso-1(RNAi) animals increased their response time by 63 ± 13%, suggesting that these animals maintain inappropriately low arousal thresholds during quiescence. (D) RNAi knockdown of the lgc-38 γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor decreased quiescence in animals lacking the unc-49 GABA A receptor. (E) RNAi knockdown of the lgc-38 in unc-49(lf) animals also decreased arousal thresholds. (F) Nonquiescent cnb-1(lf) animals were defective in their response to mechanosensory stimuli, but responded normally to dilute 1-octanol. Therefore, dilute 1-octanol response was used to demonstrate heightened arousal thresholds during quiescence.