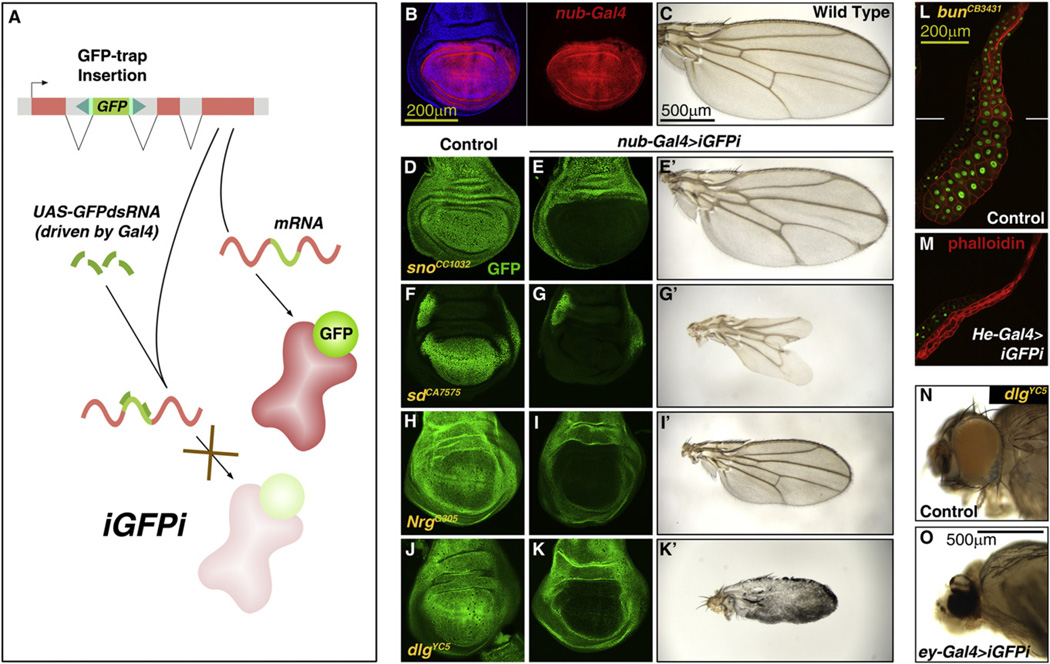
Figure 1. iGFPi Is an Effective Method to Knock Down the Expression of GFP-Trapped Proteins.
(A) Strategy of in vivo GFP interference (iGFPi). Knockdown of GFP-trapped proteins is achieved through RNAi targeting the GFP-encoding sequence.
(B) Expression of nub-Gal4 in the blade region of a third instar (L3) wing disc, revealed by Gal4-dependent expression of RFP (UAS-myrRFP, red). Cell nuclei stained with DAPI (blue) on left.
(C) Wild-type adult wing.
(D and E) iGFPi driven by nub-Gal4 (nub>iGFPi) reduces expression of GFP-trapped Strawberry notch (Sno) (E, compared to control in D; GFP in green) and causes delta-shaped termination of veins at the margin (E’).
(F and G) nub>iGFPi reduces expression of GFP-trapped Scalloped (Sd) and causes loss of distal wing tissue (G’).
(H and I) nub>iGFPi reduces expression of GFP-trapped Neuroglian (Nrg) and causes reduction in wing size (I’).
(J and K) nub>iGFPi reduces expression of GFP-trapped Discs large (Dlg) and prevents correct differentiation (K’).
(L and M) iGFPi driven by He-Gal4 in the salivary gland reduces expression of GFP-trapped Bunched (Bun) and causes reduction in cell and organ size.
(N and O) iGFPi driven by ey-Gal4 in the eye of flies expressing GFP-trapped Discs large (Dlg) prevents correct differentiation.
See also Figure S1.