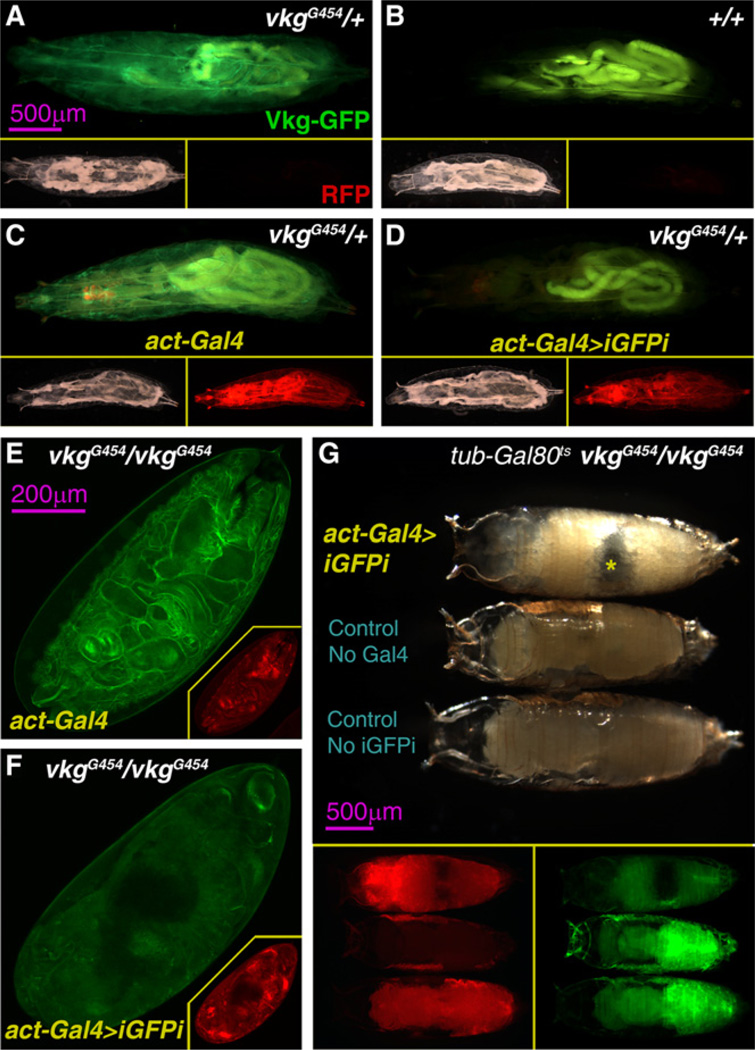
Figure 2. iGFPi Reveals a Postembryonic Requirement of Vkg.
(A–D) Vkg-GFP expression (green) in a vkgG454 heterozygous (vkgG454/+) L3 larva (A), a wild-type larva (B), an actin-Gal4 vkgG454/+ larva (C) and an actin-Gal4>iGFPi vkgG454/+ larva (D). Lower right and left subpanels show, respectively, bright-light and red fluorescence pictures of the same larvae (UAS-myrRFP, driven by actin-Gal4).
(E and F) Vkg-GFP expression (green) in 24-hr-old vkgG454/vkgG454 embryos in the presence of actin-Gal4 (E) and actin-Gal4>iGFPi (F). Red fluorescence pictures in the bottom right corner subpanels (UAS-myrRFP, red, driven by actin-Gal4).
(G) vkgG454/vkgG454 pupae of the genotypes actin>iGFPi (upper specimen), UAS-GFP.dsRNA (middle specimen) andactin-Gal4 (lower), imaged 24 hr after puparium formation. actin>iGFPi animals arrest development in prepupa stage and die (notice air bubble in abdomen indicated by asterisk). Lower subpanels show green fluorescence (Vkg-GFP) and red fluorescence (UAS-myrRFP, driven by actin-Gal4) in the same pupae.