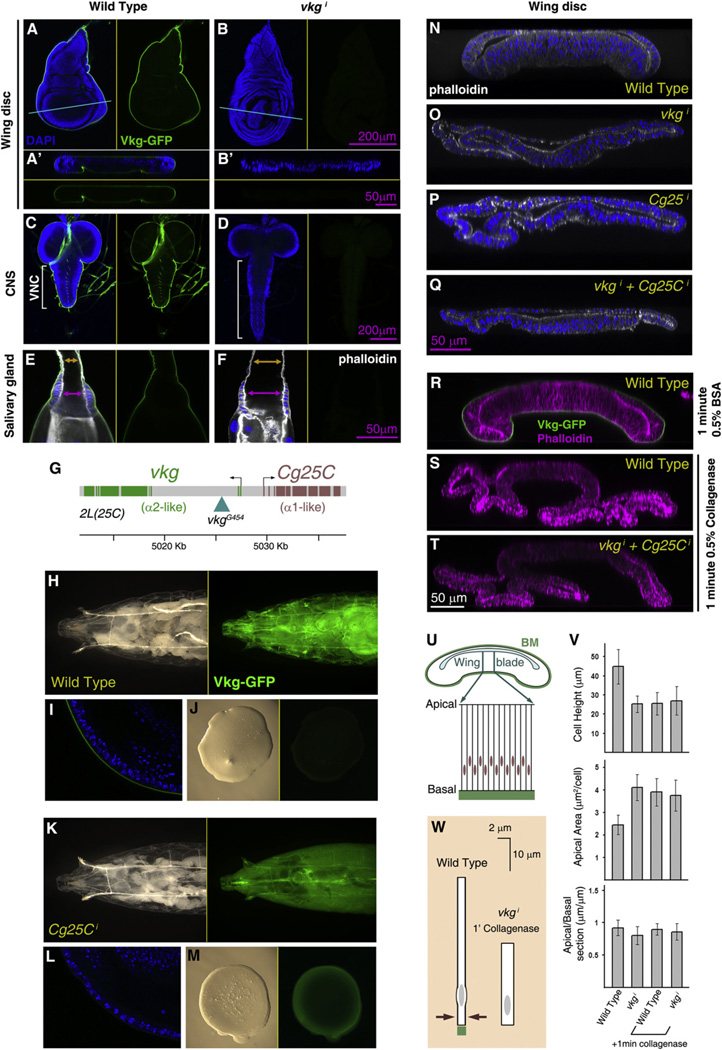
Figure 5. Collagen IV Incorporation into BMs Maintains the Shape of Larval Organs.
(A and B) Confocal images of vkgG454/+ wing discs from control larvae (A) and larvae where expression of vkg in the fat body has been knocked down during larval stages (Cg-Gal4+Gal80ts>vkgi +96 hr at 29°C). A’ and B’ show transversal sections of the same discs, as indicated by the blue lines. Vkg-GFP in green in all subpanels. Nuclei in blue (DAPI) in left (A, B) and upper (A’, B’) subpanels.
(C and D) Confocal images of the central nervous system in vkgG454/+ larvae of control (C) and Cg-Gal4+Gal80ts>vkgi genotype (D, +96 hr). Nuclei in blue (DAPI) in left subpanels. Vkg-GFP in green in all subpanels.
(E and F) Confocal images of the salivary glands in vkgG454/+ larvae of control (C) and Cg-Gal4+Gal80ts>vkgi genotype (D, +96 hr). Nuclei in blue (DAPI) and actin in white (phalloidin) in left subpanels. Vkg-GFP in green in all subpanels. Arrows indicate the width of the lumen at the duct (orange) and imaginal ring (purple). (G) Head-to-head genomic arrangement of the two Drosophila Collagen IV genes.
(H-M) Images of vkgG454/+ control larvae (H-J) and vkgG454/+ larvae where expression of Cg25C has been knocked down (K-M; CgGal4+Gal80ts>Cg25C +96 hr). Images show the anterior half of the larva (H and K), a confocal section of the wing disc (I and L) and a drop of hemolymph (J and M). Vkg-GFP in green.
(N-Q) Transversal confocal sections across wing discs from a wild-type larva (N) and larvae where expression in the fat body of vkg (O), Cg25C (P), or both (Q) has been knocked down (Cg-Gal4+Gal80ts +96 hr). Nuclei (DAPI) in blue and F-actin (phalloidin) in white.
(R-T) Transversal confocal sections across a control wing disc (R) and wing discs treated with collagenase for 1 min (S and T). Discs were from wild-type (R and S) or Cg-Gal4+Gal80ts>vkgi +96 hr (T) larvae. F-actin (phalloidin) in magenta and Vkg-GFP in green.
(U) Schematic drawing of a section through the wing disc, showing the columnar epithelial organization of the wing blade.
(V) Cell shape changes caused in the wing blade by Collagen IV knockdown and collagenase treatment. Graphs represent height of the epithelium (measured in transversal sections), apical area (measured in planar sections), and apical-to-basal length ratios (length in section of a region measured apically divided by the basal length of the same region, both in transversal sections). Measurements from at least five specimens per genotype and treatment were averaged. Differences in cell height and apical area between wild-type and the other conditions are all significant (p < 0.05 in t tests). Error bars represent standard deviations.
(W) Schematic summary of cell shape changes caused by absence of Collagen IV and collagenase treatment. See also Figure S4.