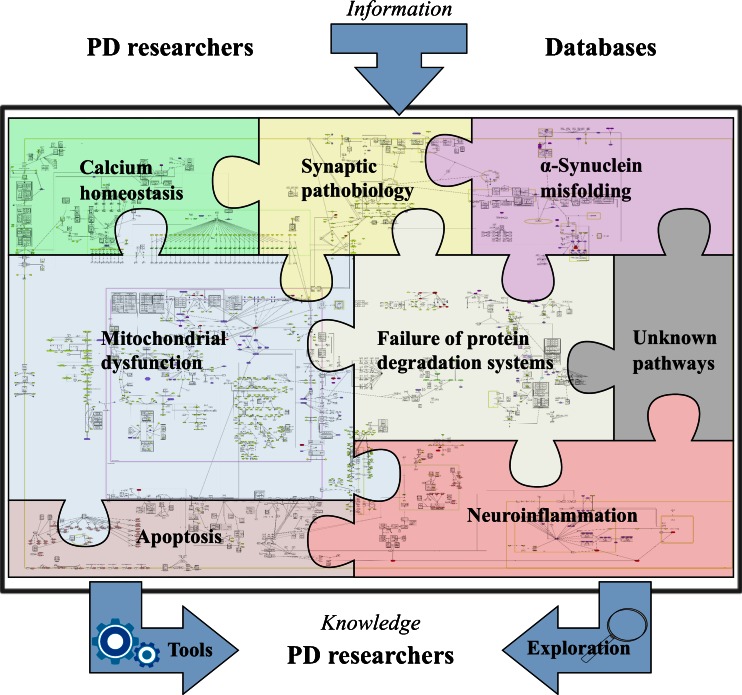
Fig. 1.
The concept of Parkinson's disease map and its possibilities. The PD map is a knowledge repository bringing together different molecular mechanisms and pathways considered to be the key players in the disease. The current focus of the map is illustrated by the pieces in the “PD puzzle” These modules include synaptic and mitochondrial dysfunction, failure of protein degradation systems, α-synuclein pathobiology and misfolding, and neuroinflammation. Processes important in PD-associated neurodegeneration, such calcium homeostasis or apoptosis, are discussed within their appropriate context in the main text, and included into the PD map pathways. The PD map is represented as a graph constructed with all gene-regulatory protein and metabolic interactions extracted from published data. Currently the map has 2,285 elements and 989 reactions supported by 429 articles and 254 entries from publicly available bioinformatic databases. It is compliant with standardized graphical representation, Systems Biology Graphical Notation (SBGN) [265]. This standardized representation of the map could become a common language for the PD research community to discuss disease-related molecular mechanisms [5]. Detailed contents of the PD map are accessible at http://minerva.uni.lu/MapViewer/map?id=pdmap (Online resource 1) as an SBML file (Online resource 2) and in Payao [264]. The map can be updated with information from the PD research community, as well as by searching bioinformatics databases. Exploration and analysis of the content has the potential to broaden knowledge on the molecular processes in PD, generate of new hypotheses on disease pathogenesis, or prioritize the most interesting areas and molecules for investigation. Approaches to facilitate this knowledge acquisition process are discussed in detail in the section “Annotation, enrichment and Analysis of the PD Map”