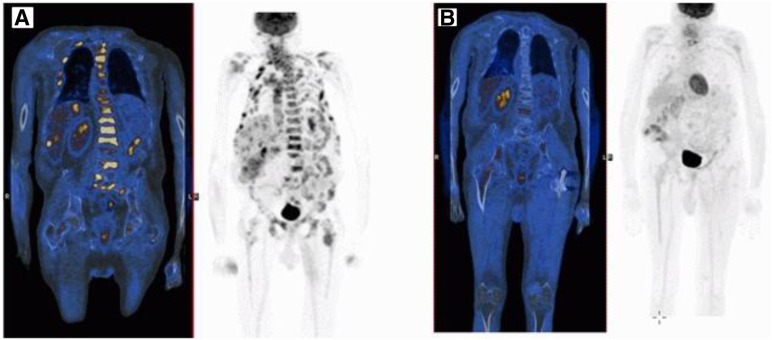
Figure 1.
Positron emission tomography-computed tomography-selected coronal slices demonstrate multiple foci of pathological increased fludeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake in lytic and sclerotic bone lesions and in hypodense liver lesions (A) and significant improvement with few low-intensity foci of FDG uptake in the skeleton and no evidence of liver metastases (B) after 6 months of treatment.