Abstract
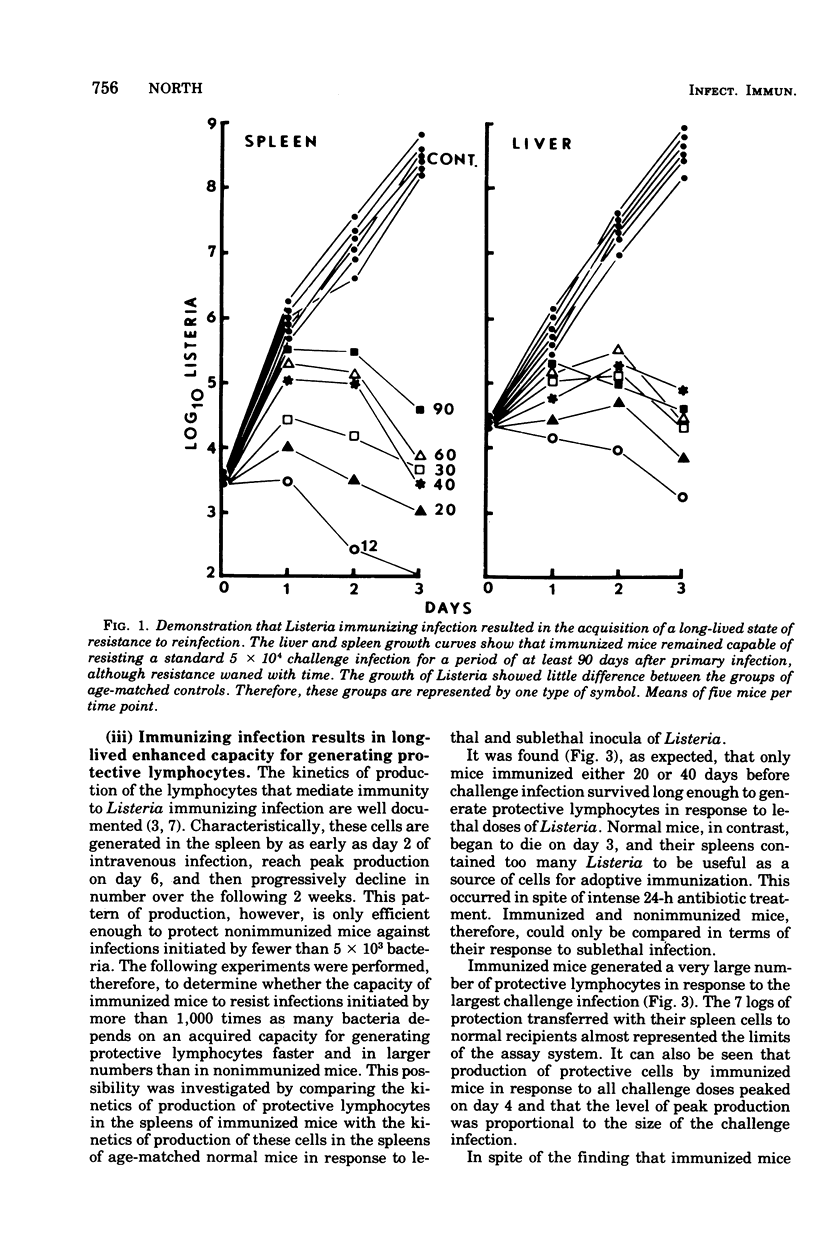
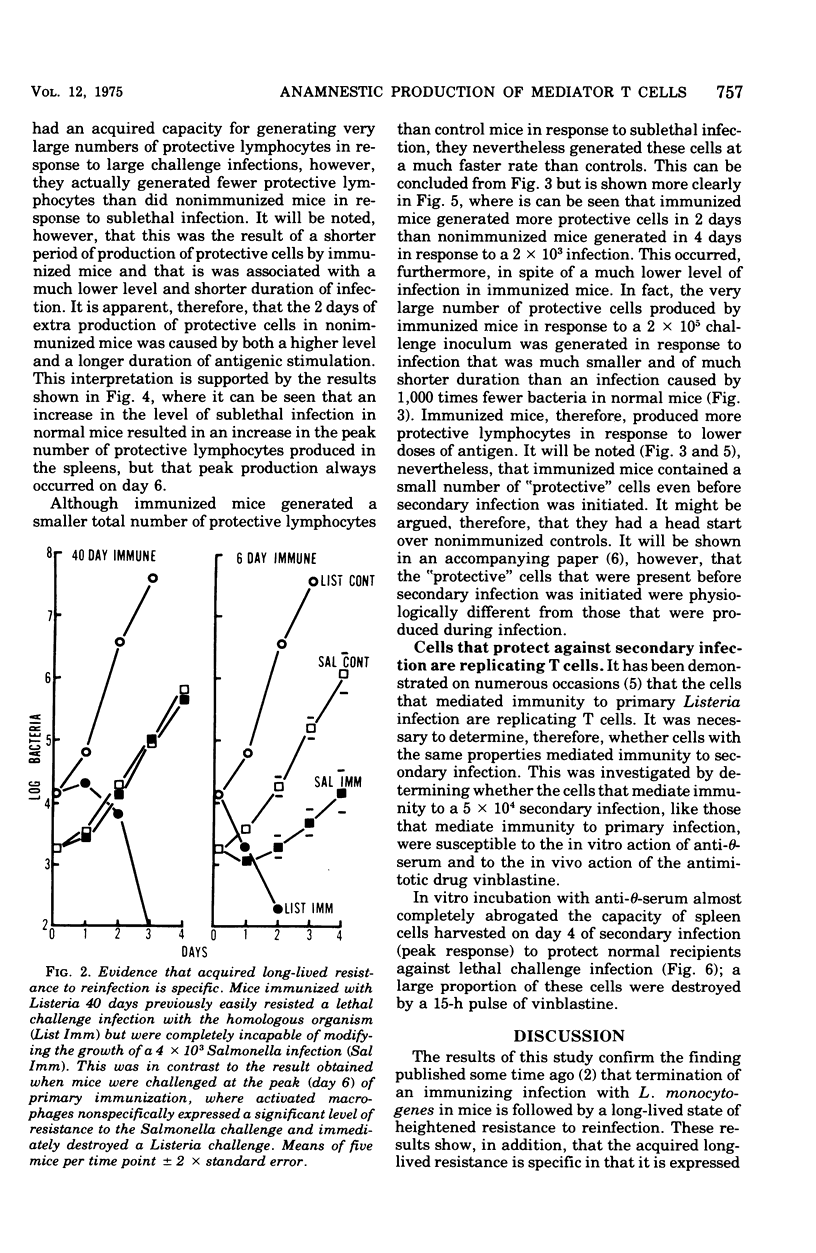
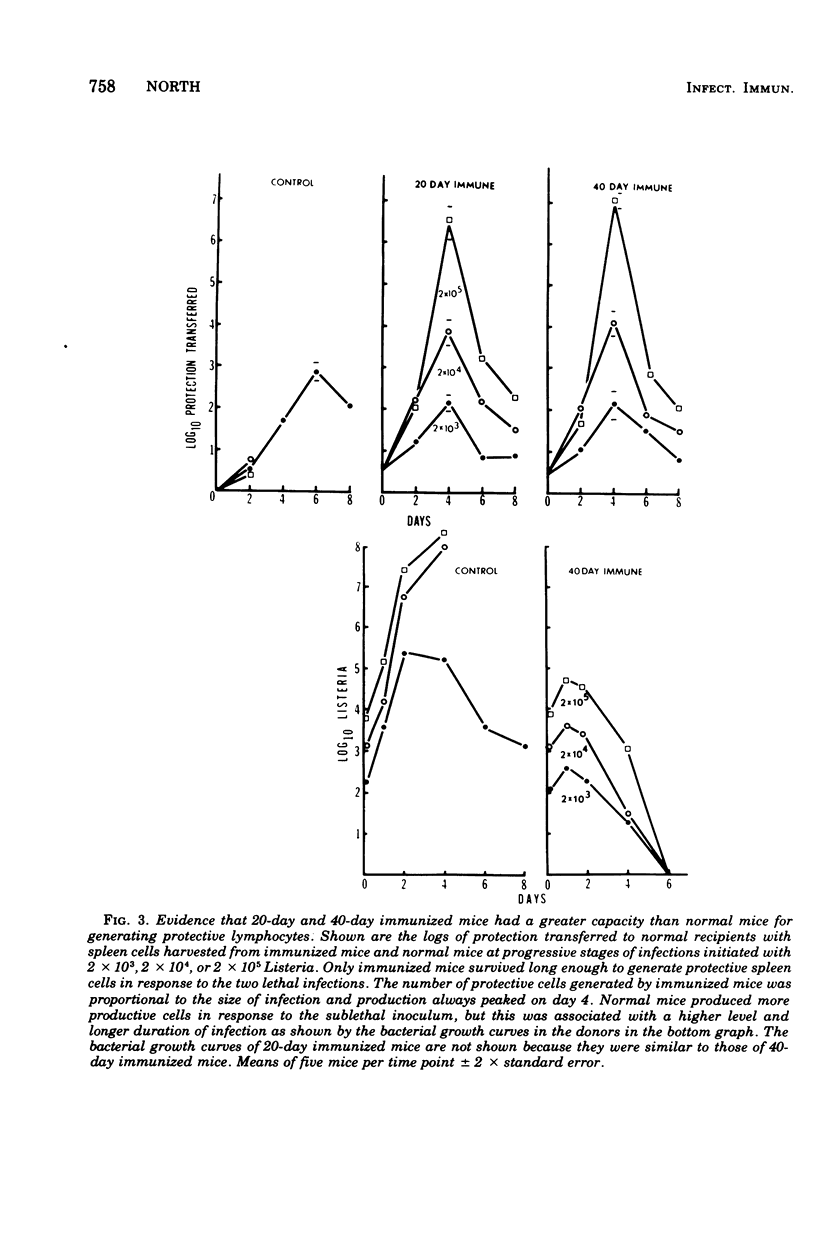
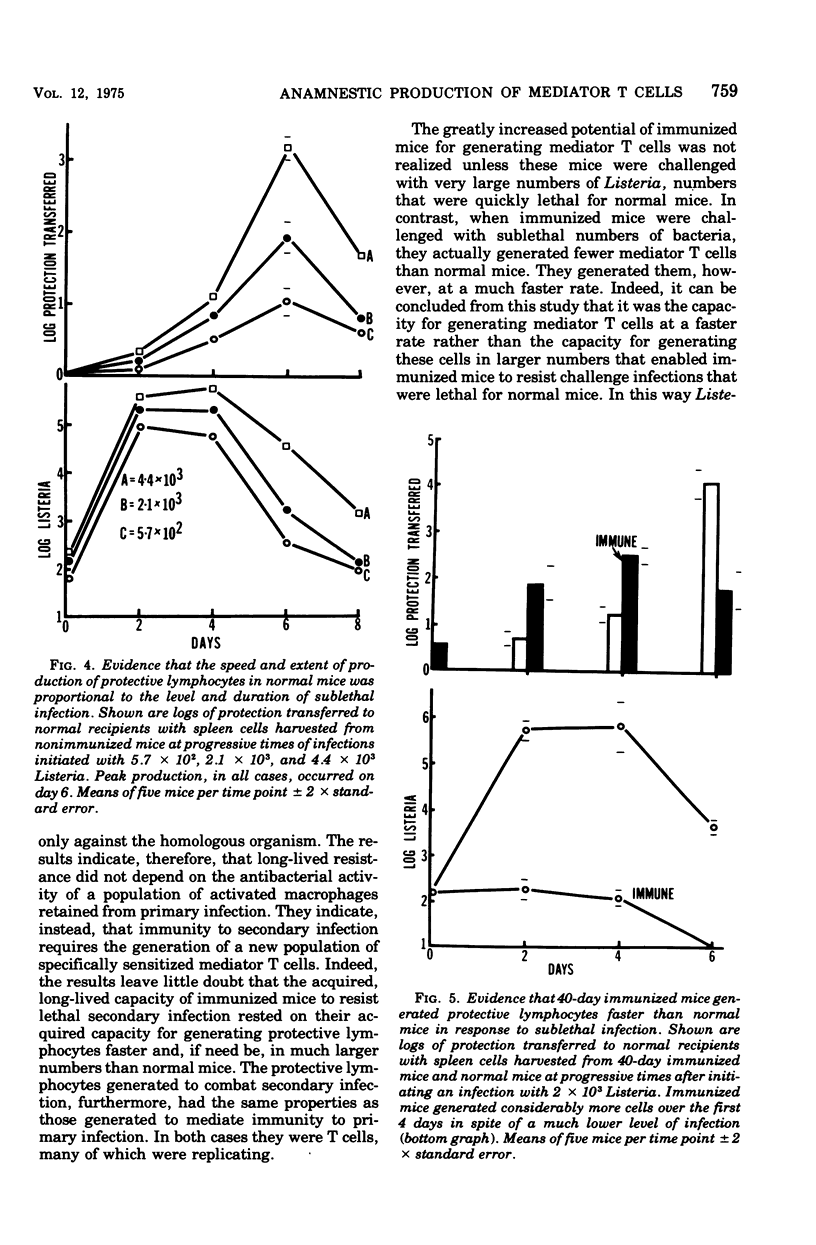
Mice that survived an immunizing infection with Listeria monocytogenes remained specifically resistant to lethal secondary infection for several months. This acquired, long-lived state of resistance was not dependent on activated macrophages that remained after the primary response. It depended, instead, on an acquired long-lived capacity on the part of immunized mice for generating mediator T cells faster and in larger numbers than normal mice. The number of mediator T cells generated in response to secondary infection was proportional to the level of infection. The results suggest that the accelerated production of mediator T cells that occurs in response to secondary infection represents the expression of a state of immunological T-cell memory.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen A., Schlesinger M. Absorption of guinea pig serum with agar. A method for elimination of itscytotoxicity for murine thymus cells. Transplantation. 1970 Jul;10(1):130–132. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197007000-00027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. Cellular mediators of anti-Listeria immunity as an enlarged population of short lived, replicating T cells. Kinetics of their production. J Exp Med. 1973 Aug 1;138(2):342–355. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.2.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J., Deissler J. F. Nature of "memory" in T-cell mediated antibacterial immunity: cellular parameters that distinguish between the active immune response and a state of "memory". Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):761–767. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.761-767.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. Importance of thymus-derived lymphocytes in cell-mediated immunity to infection. Cell Immunol. 1973 Apr;7(1):166–176. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J., Spitalny G. Inflammatory lymphocyte in cell-mediated antibacterial immunity: factors governing the accumulation of mediator T cells in peritoneal exudates. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):489–498. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.489-498.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valeriote F. A., Bruce W. R. An in vitro assay for growth-inhibiting activity of vinblastine. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1965 Nov;35(5):851–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


