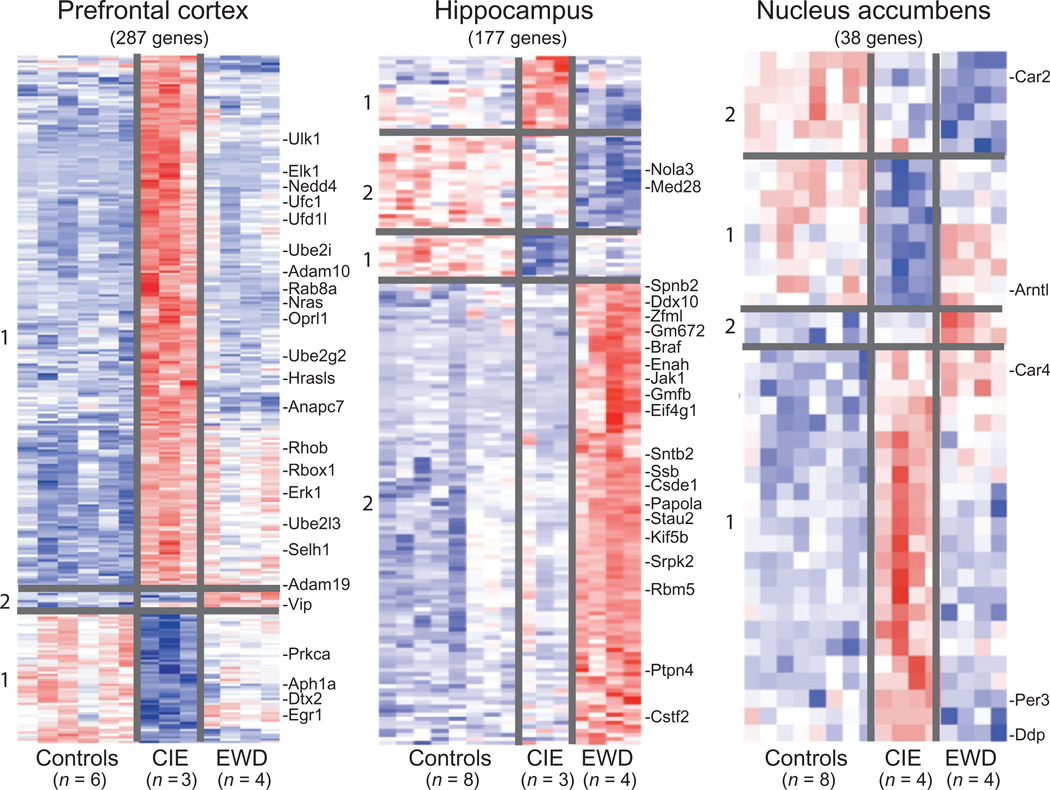
Figure 1.
Expression profile (heat map) of the total number of genes associated with chronic intermittent ethanol (CIE) exposure and ethanol early withdrawal (EWD) in the prefrontal cortex (287 genes), hippocampus (177 genes) and nucleus accumbens (38 genes) of C57BL/6J mice. Duplicate pooled samples were hybridized to an individual microarray chip for each of the three brain regions studied. Control samples were collapsed and compared across conditions [i.e. controls (n = 6–8) versus CIE (n = 3–4) versus EWD (n = 4)] using multivariate significance analysis of microarrays with a false discovery rate of < 10%. Genes are hierarchically clustered and colored according to their expression values on a continuous scale from blue (under-expression) to red (over-expression). Red-blue midtones (e.g. white) indicate basal expression of genes compared with controls. Gene cluster 1:genes associated with CIE (i.e. EtOH responsive). Gene cluster 2:genes associated with EWD (i.e. withdrawal responsive). Over-responsive genes of functional relevance are listed on the side of each heat map and described further in Tables 1–3. The complete list of all genes and expression values for each of the brain regions is listed in Supporting Information Tables S2–S4