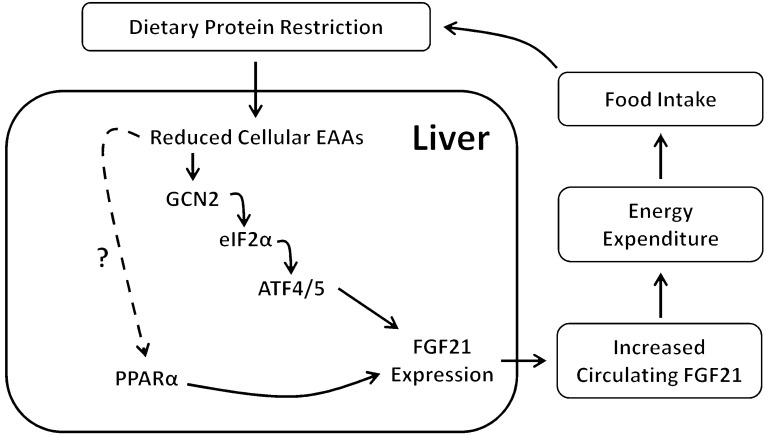
Figure 6. Hypothetical model of protein-dependent regulation of FGF21 and its effects on food intake and EE.
Reduced consumption of dietary protein leads to reduced delivery of amino acids to the liver, activating the kinase GCN2 and leading to increased eIF2α phosphorylation and activation of ATF4/ATF5. ATF4/5 bind AAREs within the FGF21 promoter, leading to increased liver FGF21 production and increased circulating FGF21. PPARα is also required for normal levels of circulating FGF21. Finally, increased circulating levels of FGF21 increase EE and food intake and also alter body weight gain and body composition.