Figure 2.
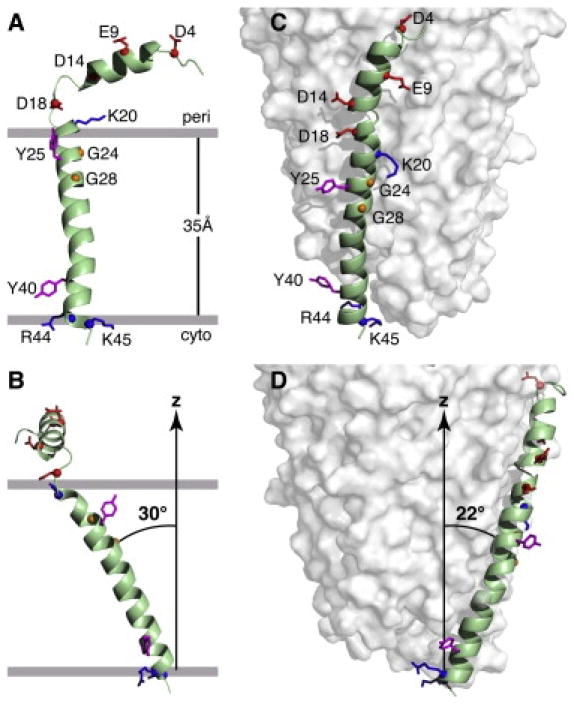
Structures of the Pf1 coat protein. A. and B. The membrane-bound form of the protein. C. and D. The structural form in the intact bacteriophage particle. In the membrane-bound form of the protein, the acidic N-terminus region is exposed to the bacterial periplasmic space (peri) and the basic C-terminal region is exposed to the cytoplasm (cyto). Acidic residues (Asp and Glu) are shown in red, conserved glycine residues in the transmembrane helix are in yellow, basic residues (Arg and Lys) are in blue, and interfacial tyrosines are in pink. Residues R44 and K45 face the cytoplasm in the membrane-bound form and the DNA on the interior of the bacteriophage particles. B. and D. Images obtained by 90o rotation of A and C around the z axis. From Park et al (2010).
