Figure 1.
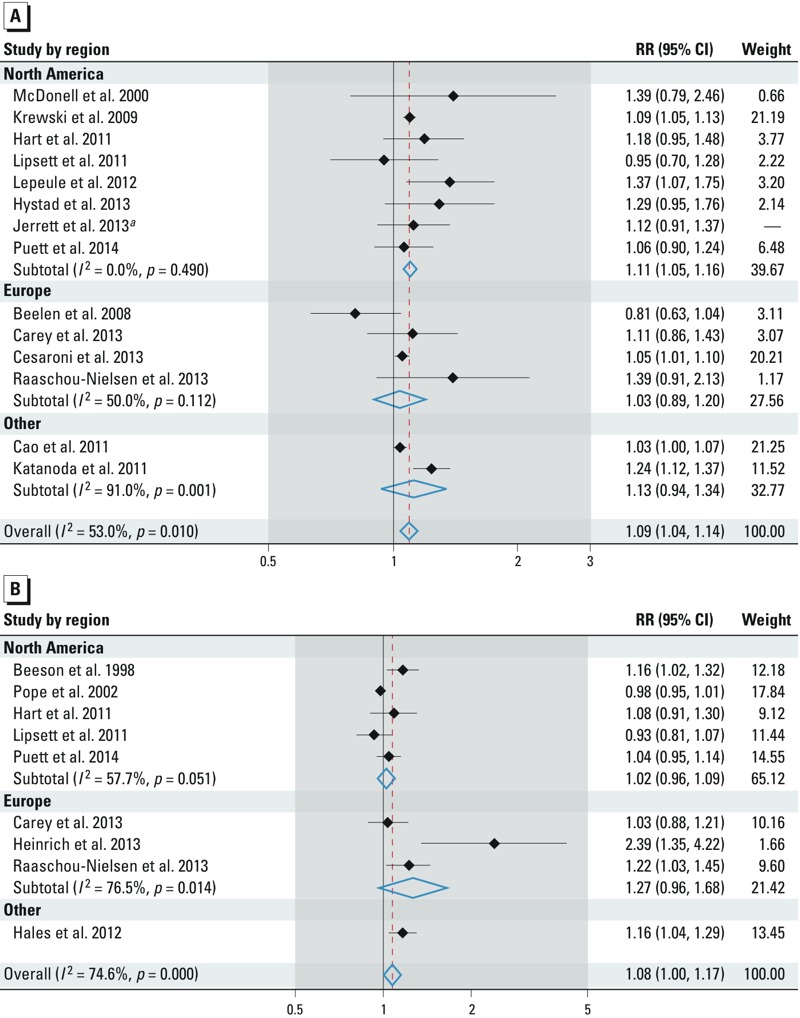
Estimates of lung cancer risk associated a 10-μg/m3 change in exposure to PM2.5 (A) and PM10 (B) overall and by geographic region of study. Weights represent the contribution of each study effect estimate to the overall meta-estimate. aJerrett et al. (2013) contributes neither to the overall nor to the continent-specific meta-estimates; it is only included here for visualization.
