Fig. 6. Eupatorin exerts a similar effect as UE-12 crude extract.
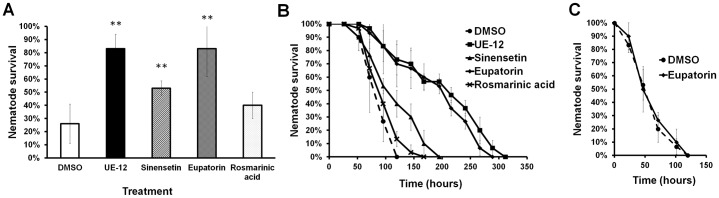
(A) S. aureus infection assay of wild-type nematodes exposed to sinensetin, eupatorin and rosmarinic acid, respectively. The graph depicts the mean percentage of survival ± SD at 96 hpi of three replicates from a representative of two individual experiments. (B) Survival of S. aureus-infected worms is significantly improved over time upon supplementation with eupatorin. In a pair-wise comparison to untreated animals (DMSO) using log-rank tests, the difference is significant (p<0.0001). (C) The effect of eupatorin is completely impaired in pmk-1 (km25) mutants. The graph shows the mean ± SD of six replicates (20 nematodes/replicate) from a representative of three independent assays. **A significant difference between untreated (DMSO) and treated worms (p<0.05).
