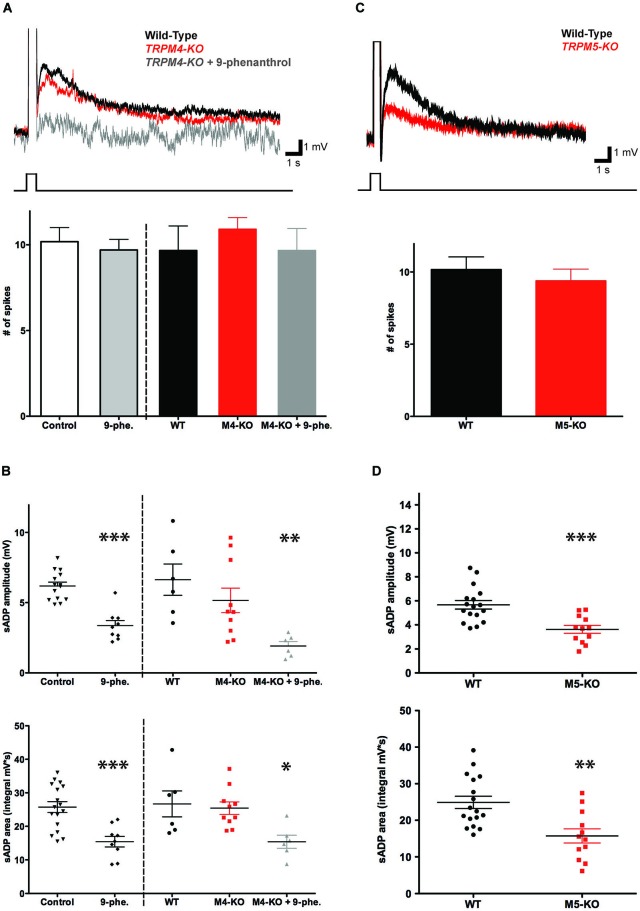
Figure 5.
TRPM5 but not TRPM4 contributes to the CCh-induced sADP. (A) TRPM4 deletion did not significantly alter the sADP. Inset: superimposed representative traces show sADP induced by a depolarizing current step (200 pA, 500 ms) in CCh for wild-type littermate control mice (black trace), Trpm4−/− mice (red trace) and Trpm4−/− mice in the presence of 9-phenanthrol (dark gray trace). Initial Vm was −66 mV. Bar graph, there was no statistically significant difference in numbers of spikes in wild-type mice under control conditions vs. in the presence of 9-phenanthrol (n = 10–22, P = 0.71). There were no significant differences in number of spikes among wild-type (WT) mice or Trpm4−/− mice (M4-KO) under control conditions or in presence of 9-phenanthrol (M4-KO + 9-phe.); n = 6–11, P = 0.39 and P = 1 respectively. (B) Genetic deletion of TRPM4 did not significantly reduce sADP amplitude (top graph; n = 6–10, P = 0.31) or sADP area (bottom graph; n = 6–10, P = 0.74). However, application of 9-phenanthrol in both control and Trpm4−/− mice decreased significantly peak sADP amplitude (wild-type control vs. 9-phenanthrol, n = 9–17, *** P < 0.001; wild-type control vs. KO with 9-phenanthrol, n = 6, ** P < 0.01) and sADP area (in control vs. with 9-phenanthrol, n = 9–17, *** P < 0.001; in WT vs. KO with 9-phenanthrol, n = 6, * P < 0.05) by a depolarizing step current (200 pA for 500 ms). (C) TRPM5 deletion reduced the sADP. Inset: sADP induced by depolarizing current (200 pA, 500 ms) in CCh in wild-type littermate control mice (black trace) and Trpm5−/− KO mice (red trace). Initial Vm was −65 mV. Bar graph, TRPM5 deletion (M5-KO) had no effect on number of spikes during the depolarizing step (n = 13–18, P = 0.54). (D) Deletion of TRPM5 significantly decreased sADP amplitude (top graph; n = 12–17, *** P < 0.001) and area (bottom graph; n = 12–17, ** P < 0.01).