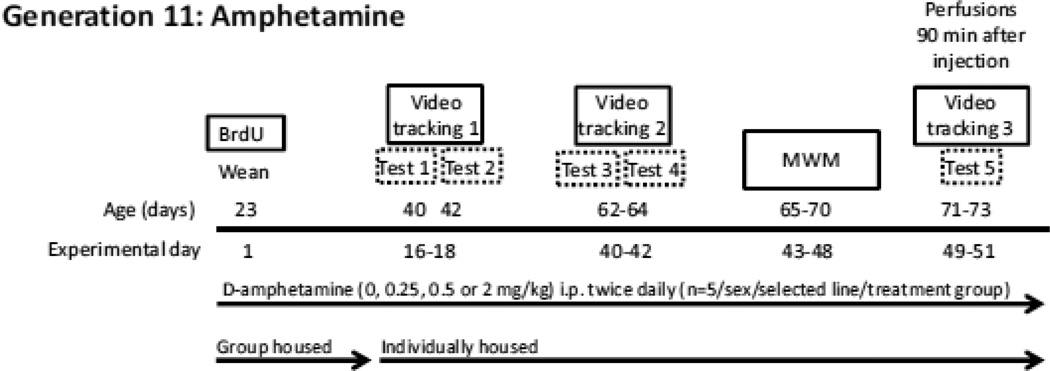
Figure 1. Time-course for Experiment 2.
Animals were administered twice daily i.p. injections of saline, 0.25, 0.5, or 2 mg/kg d-amphetamine (n= 5 per sex/line/treatment = 80 total) for 49–51 days, starting from when the mice were 23 days old (Experimental day 1) and continuing until they were 73 days old (Experimental day 51). Mice also received 10 daily i.p. injections of BrdU (50 mg/kg) to label dividing cells on experimental days 1–10 (mouse age 23–32 days old). On Experimental days 16–18 and 40–42, 64 mice/80 total were placed in specialized cages which allowed for video tracking of home cage locomotor behavior (Tests 1–4). Prior to the first locomotor activity session, mice were separated from group housing conditions and individually housed to allow for individual locomotor tracking. Mice then remained singly housed throughout the duration of the experiment. On Experimental days 43–48, 40 mice/80 total were tested on the Morris water maze (MWM). On Experimental days 49–51, the same 64 mice were placed in the specialized home cages to allow for video tracking one final time (Test 5), then staggered over the course of the next two days for systemic perfusions with 4% paraformaldehyde exactly 90 min. following the final injection for each mouse.