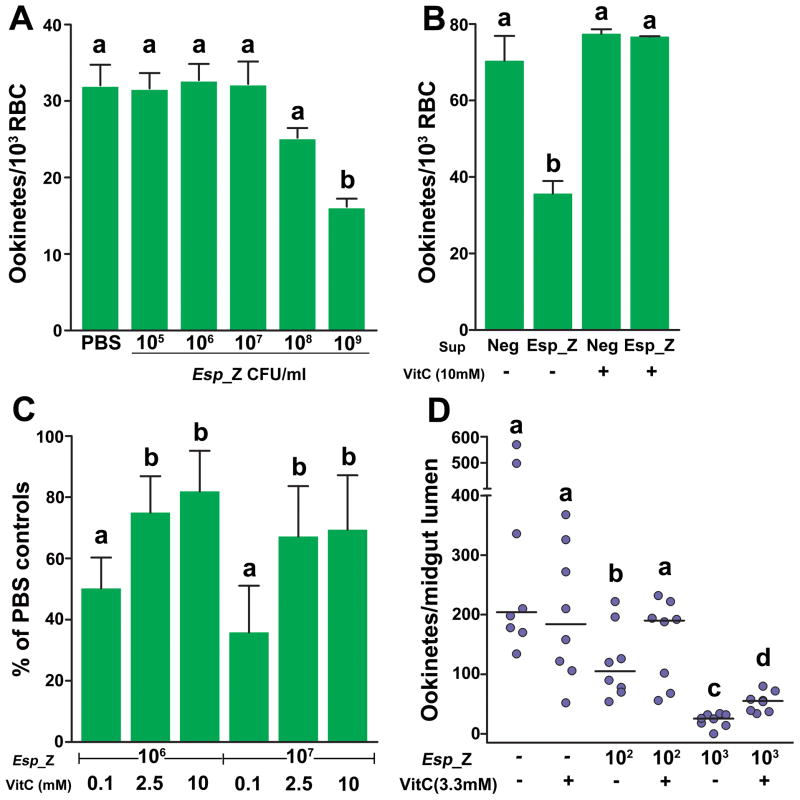
Figure 3. Involvement of ROS generation by Esp_Z in inhibition of Plasmodium development.
(A) Effect of physical separation of Esp_Z and parasites on P. berghei ookinete formation. (B) Effect of filtered culture supernatant and addition of vitamin C on P. berghei ookinete formation. Sup=supernatant; Neg=supernatant from a bacteria-negative culture; VitC=vitamin C. For (A–B), bars represent the mean ± the standard deviation. (C–D) Effect of vitamin C addition on P. berghei ookinete formation in vitro (C) and P. falciparum ookinete formation in A. gambiae midguts (D). For (C), bars represent the mean ± the standard deviation in percentage of the number of ookinetes formed in bacteria-treated groups as compared to PBS-treated controls. For (D), circles represent the number of ookinetes from an individual mosquito and horizontal lines indicate the median number of parasites per midgut. For all figures, statistical significance is represented by letters above each column, with different letters signifying distinct statistical groups (p<0.05; unpaired t-test for (A–C); Mann-Whitney test for (D)).