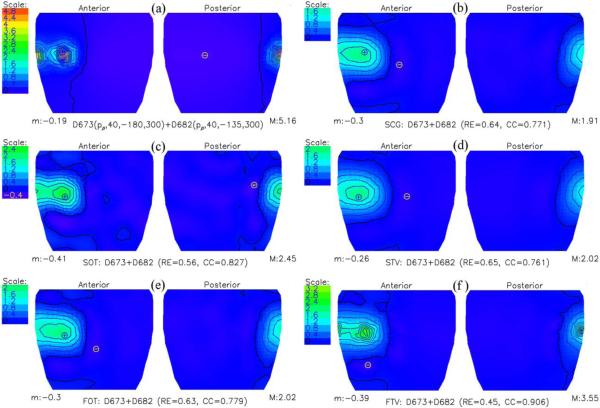
Fig. 2.
Cylindrical-cage potential distribution due to a pair of parallel dipoles, 30.6 mm apart, positioned close to the surface of the cage. (a) Cylindrical cage potentials calculated directly. (b through f) Inversely computed cylindrical cage potentials using a second-order conjugate gradient iterative method (SCG), second-order Tikhonov regularization (SOT), total variation algorithm, whose gradient operator was replaced by a Laplacian operator (STV), first-order Tikhonov regularization (FOT), and first-order total variation technique (FTV), respectively. Two extrema were reconstructed clearly only by SOT and FTV. “M” denotes maximum potential and “m” denotes minimum potential.