Abstract
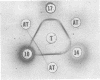
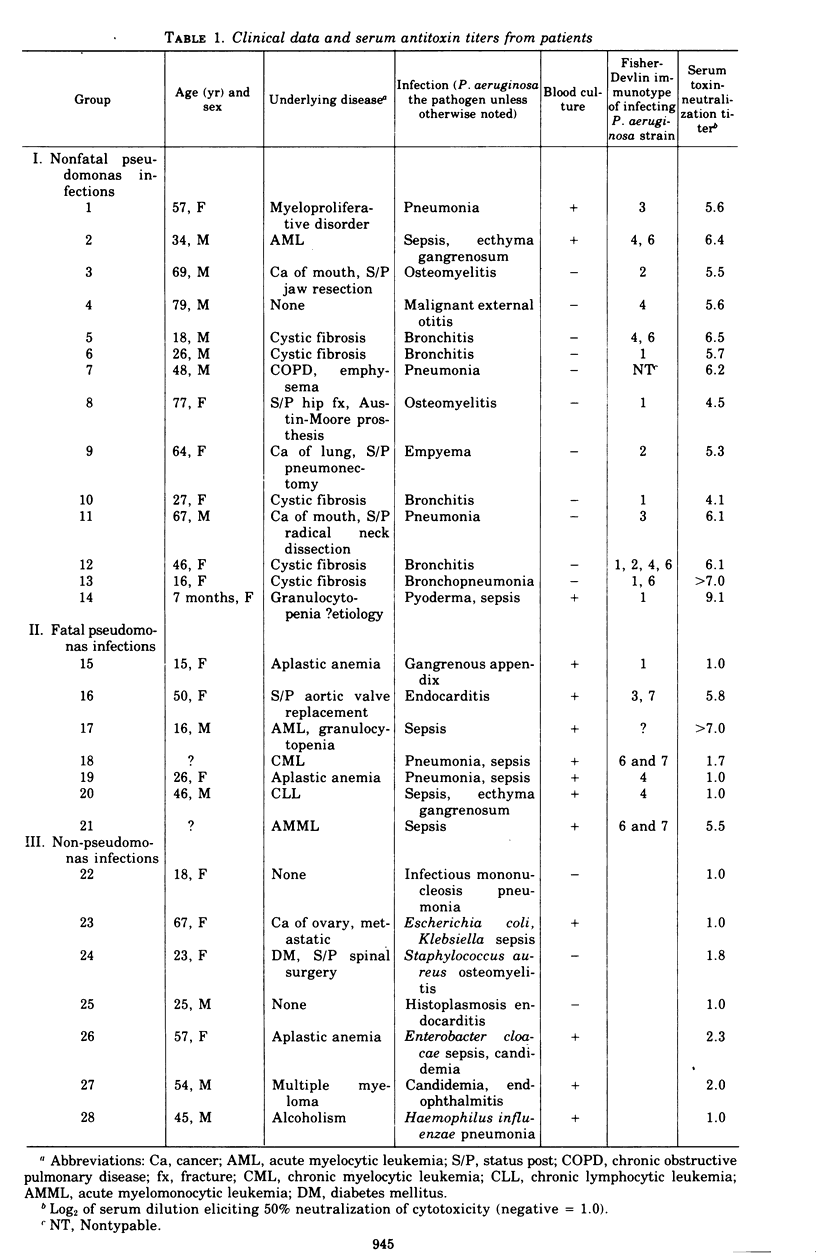
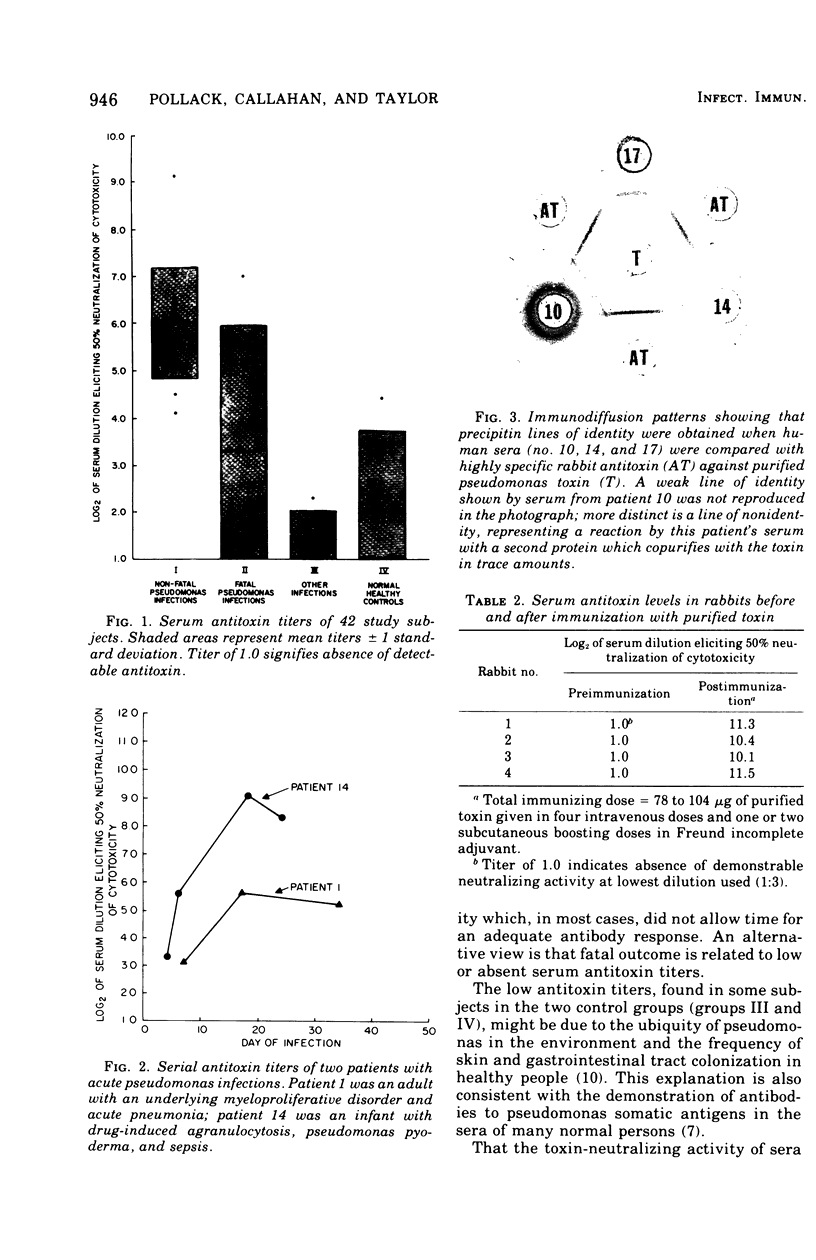
Antibody to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin was detected in human sera by using a cytotoxicity-neutralization assay. Serum antitoxin was present in high titer in all 14 patients who recovered from serious pseudomonas infections (log2 of 50% neutralization titer, mean +/- standard deviation = 6.0 +/- 1.2). In contrast, serum antitoxin was present in lower titer in four of seven patients with fatal pseudomonas infections (3.3 +/- 2.7, P less than 0.005), in 3 of 7 patients with non-pseudomonas infections (1.4 +/- 0.6 P less than 0.001), and in 6 of 14 normal control subjects (2.0 +/- 1.3, P less than 0.001). Fourfold or greater serum antitoxin rises were demonstrated in two survivors of acute infections, and toxin-neutralizing activity was associated with the immunoglobulin G fraction of human sera. Immunization of rabbits with purified exotoxin also induced high antitoxin titers.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atik M., Liu P. V., Hanson B. A., Amini S., Rosenberg C. F. Pseudomonas exotoxin shock. A preliminary report of studies in dogs. JAMA. 1968 Jul 15;205(3):134–140. doi: 10.1001/jama.205.3.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan L. T., 3rd Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin: purification by preparative polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and the development of a highly specific antitoxin serum. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):55–61. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.55-61.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan L. T., 3rd Purification and characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):113–118. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.113-118.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEUTSCH H. F., MORTON J. I. Dissociation of human serum macroglobulins. Science. 1957 Mar 29;125(3248):600–601. doi: 10.1126/science.125.3248.600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diener B., Carrick L., Jr, Berk R. S. In vivo studies with collagenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):212–217. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.212-217.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyke J. W., Berk R. S. Comparative studies on Pseudomonas aeruginosa endotoxin. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1973;13(4):307–313. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630130404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAINES S., LANDY M. Prevalence of antibody to Pseudomonas in normal human sera. J Bacteriol. 1955 Jun;69(6):628–633. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.6.628-633.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzman R. J., Segall M., Bach M. L., Bach F. H. Histocompatibility matching. VI. Miniaturization of the mixed leukocyte culture test: a preliminary report. Transplantation. 1971 Mar;11(3):268–273. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197103000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma J. Y. The protein moiety of the endotoxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1968;8(3):227–248. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630080310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Kabat D. NAD-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin,. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KILLANDER J. SEPARATION OF HUMAN HEME- AND HEMOGLOBIN-BINDING PLASMA PROTEINS, CERULOPLASMIN AND ALBUMIN BY GEL FILTRATION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Oct 9;93:1–14. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90254-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaharajo K., Homma J. Y., Aoyama Y., Morihara K. In vivo studies on protease and elastase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Jpn J Exp Med. 1975 Apr;45(2):89–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen R. C., Callahan L. T., 3rd, Ahmed A., Sell K. W. Use of microculture plates and the multiple automated sample harvester for in vitro microassay of bacterial toxins. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):326–327. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.326-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU P. V., ABE Y., BATES J. L. The roles of various fractions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in its pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1961 Mar-Apr;108:218–228. doi: 10.1093/infdis/108.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. The roles of various fractions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in its pathogenesis. 3. Identity of the lethal toxins produced in vitro and in vivo. J Infect Dis. 1966 Oct;116(4):481–489. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.4.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. The roles of various fractions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in its pathogenesis. II. Effects of lecithinase and protease. J Infect Dis. 1966 Feb;116(1):112–116. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.1.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinke G., Barum J., Rosenberg B., Berk R. In Vivo Studies with the Partially Purified Protease (Elastase) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):583–589. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.583-589.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels G. B., Eagon R. G. The effect of ethylenediaminetetraacetate and lysozyme on isolated lipopolysaccharide from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Jul;122(3):866–868. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody M. R., Young V. M., Kenton D. M., Vermeulen G. D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a center for cancer research. I. Distribution of intraspecies types from human and environmental sources. J Infect Dis. 1972 Feb;125(2):95–101. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.2.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Gordon F. B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin: effect on cell cultures. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jun;125(6):631–636. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.6.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Shackelford A. H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin in mice: localization and effect on protein synthesis. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):540–546. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.540-546.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]