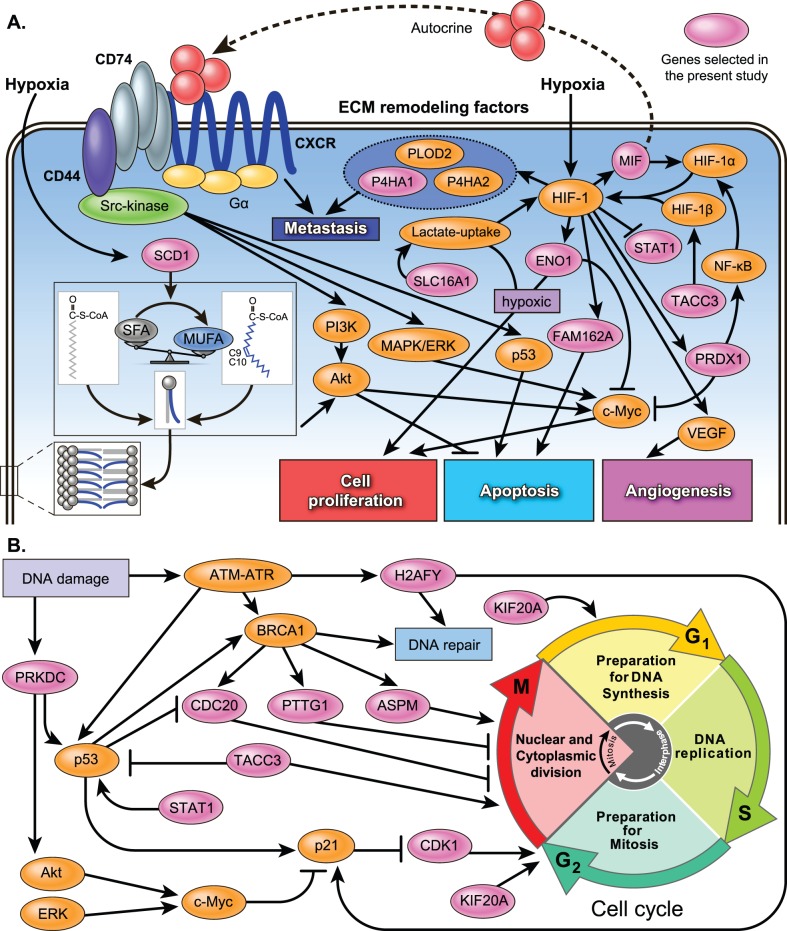
Figure 8. A hypothetical regulation model of metabolic and signaling control in highly malignant STS.
(A) Signaling pathways, excluding cell cycle and DNA repair. (B) Cell cycle and DNA repair pathways. The pink oval indicates the genes selected in the present study. MUFA, monounsaturated fatty acid; SFA, saturated fatty acid; SCD1, stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1; MIF, macrophage migration inhibitory factor; CXCR, CXC chemokine receptor; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; MAPK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; ERK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; PTTG1, pituitary tumor-transforming 1; ASPM, abnormal spindle-like microcephaly-associated protein; CDC20, cell division cycle protein 20; KIF20A, kinesin family member 20A; ENO1, enolase 1; P4HA, prolyl 4-hydroxylase subunit α; PRDX1, peroxiredoxin 1; FAM162A, family with sequence similarity 162, member A; STAT1, signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; CDK1, cyclin-dependent kinase 1; TACC3, transforming, acidic coiled-coil containing protein 3; PRKDC, protein kinase, DNA-activated, catalytic polypeptide; H2AFY, H2A histone family, member Y; SLC16A1, solute carrier family 16, member 1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; HIF, hypoxia inducible factor; PLOD2, procollagen-lysine,2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase 2; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B.