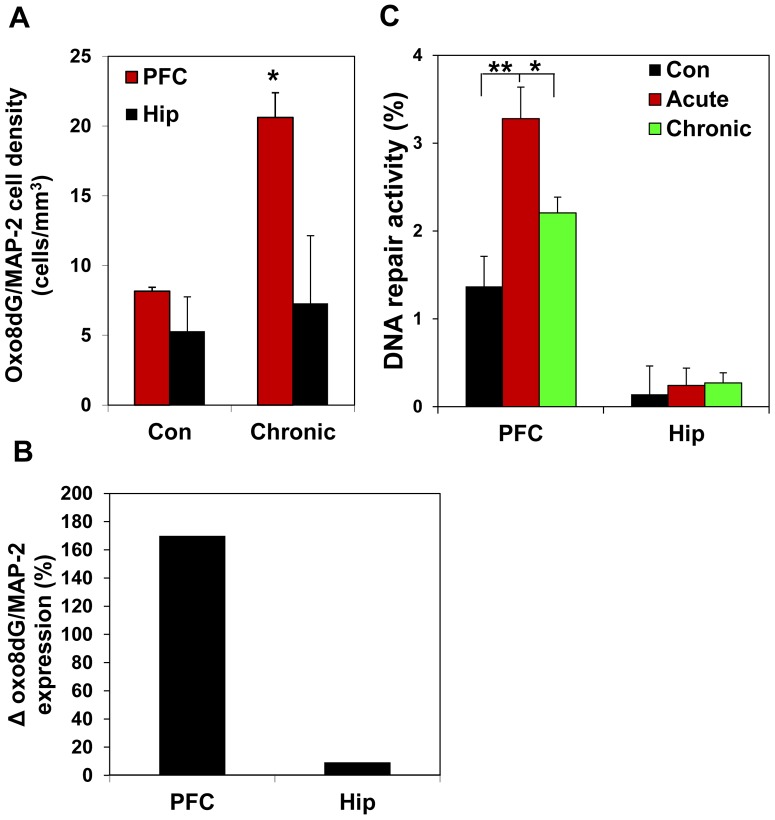
Figure 2. PFC is more vulnerable to ethanol-induced oxidative stress than hippocampus.
(A) oxo-8dG expression in neurons (neuronal marker MAP-2) was quantified in PFC and hippocampus (Hip) by stereological counting. Neither the number of neurons nor volumes of the brain structures were affected. Values are mean ± SEM; *p<0.01. (B) Oxo-8dG expression in neurons normalized to corresponding controls (Δ). Note significantly higher density of oxo-8dG -labeled neurons and Δ in PFC, compared with hippocampus of ethanol-exposed mice. (C) DNA repair activity in response to oxidative DNA damage (oxo-8dG) assessed by qPCR in whole cell extracts obtained from PFC and hippocampus (Hip) of control mice and mice exposed to acute or chronic ethanol. Values are means ± SEM; *p<0.05, **p<0.01. Note the response to oxidative DNA damage by PFC lysate is significantly stronger than those in the hippocampus.