FIGURE 3.
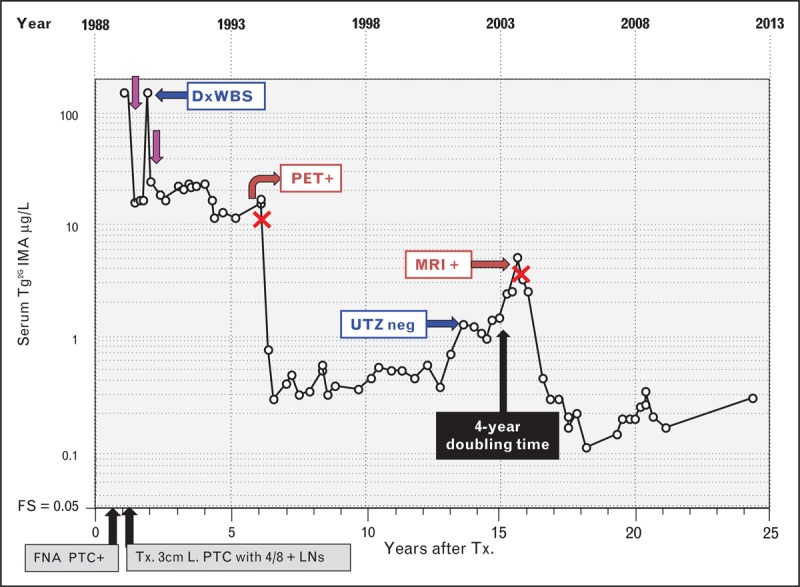
Serum (second-generation) thyroglobulin immunometric assay monitoring of a patient with persistent and recurrent papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) and negative thyroglobulin autoantibodies. This female patient presented in 1988 at age 42 with a 3-month history of an enlarging anterior neck mass. PTC was diagnosed by fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNA) and treated by total thyroidectomy to remove a 3 cm tumor, together with 4 out of 8 PTC-positive lymph nodes. Preoperative serum thyroglobulin was elevated (154 μg/L) suggesting that postoperative serum thyroglobulin monitoring would be efficacious. Serum basal Tg2GIMA measurements made during 25 years of postoperative thyroglobulin monitoring are shown (Beckman Access Tg2GIMA measurement of frozen archived specimens [37▪▪]) during thyroid hormone therapy (TSH < 0.05 mIU/L). Following an initial RAI treatment (∼150 mCi) (purple arrows), persistent disease was suspected by inappropriately high thyroglobulin values (15–20 μg/L). Despite a negative diagnostic whole body scan (DxWBS), the elevated thyroglobulin prompted a second RAI treatment (150 mCi) that revealed foci of thyroid uptake and a submandibular lymph node on the post-treatment scan. However, the two RAI treatments had little effect on the elevated serum thyroglobulin, which remained persistently elevated for 5 years prompting computed tomography scans of the neck and chest (negative) followed by a PET scan that revealed a lymph node, confirmed by FNA as positive for PTC. During a left jugular dissection (surgeries indicated by red crosses), a 1.5 cm lymph node metastasis was removed producing a significant fall in serum Tg2GIMA into the 0.3–0.5 μg/L range, a level that was sustained for approximately 5-years. Thereafter, despite continued TSH suppression, Tg2GIMA rose with an approximate 4-year doubling time prompting an ultrasound investigation (negative) and later an MRI that detected a single 1.0 cm lymph node metastasis that was removed during a level 2, 3 and 5 neck dissection. Thereafter, serum Tg2GIMA values fell to the 0.20–0.40 μg/L range but remained detectable. The persistence of the detectable serum Tg2GIMA despite two doses of RAI suggests that disease may still be present. FNA, fine-needle aspiration; FS, functional sensitivity; LNs, lymph nodes; PTC, papillary histotype; RAI, radioiodine; Tg2GIMA, (second-generation) thyroglobulin immunometric assay; TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone; Tx., thyroidectomy.
