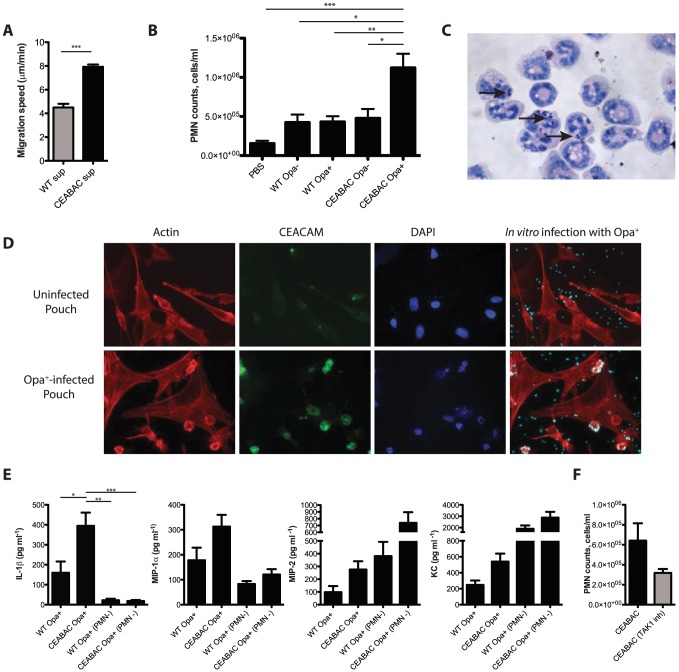
Figure 6. CEACAM binding stimulates the inflammatory response to N. gonorrhoeae in vivo.
(A) Neutrophil migration assay. PMN migration speed towards N. gonorrhoeae infected CEABAC or WT neutrophil-derived supernatants was measured using a Zigmond chamber. One-Way ANOVA (with Tukey's post-test) was performed for relevant samples, ***P<0.001 (B) Neutrophil infiltration is more pronounced in human CEACAM-expressing mice in an infected subcutaneous air pouch model. Manual neutrophil counts of wash fluids collected from air pouches. ‘PBS’ denotes mice injected with sterile PBS. One-Way ANOVA was performed for relevant samples, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (C) Giemsa-Wright stain of wash fluid collected from CEABAC air pouch infected with Opa+ N. gonorrhoeae. The arrows point towards N. gonorrhoeae inside the neutrophil. (D) Neutrophil-expressed CEACAMs mediate N. gonorrhoeae binding within the air pouch. Cells from trypsinized air pouches were grown on coverslips in the presence of antibiotics, and infected in vitro with Opa+ N. gonorrhoeae. Cells were visualized by staining for filamentous actin [16], CEACAMs (green), DNA (blue) and bacteria (cyan). (E) Levels of MIP-1α, MIP-2, KC, and IL-1β were measured in wash fluids collected from air pouches. PMN− refers to mice in which neutrophils were depleted by administration of the Gr1-specific clone RB6-8C5 antibody one day prior to infection with Opa+ N. gonorrhoeae. One-Way ANOVA (with Tukey's post-test) was performed for relevant samples, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (F) Inhibition of pro-inflammatory signaling reduces neutrophil infiltration into the air pouch. Neutrophil counts of wash fluids collected from CEABAC mice infected with Opa+ N. gonorrhoeae in the presence or absence of TAK1 inhibitor.