Figure 2. Serum inhibition of PLY requires cholesterol with a free 3β-hydroxyl.
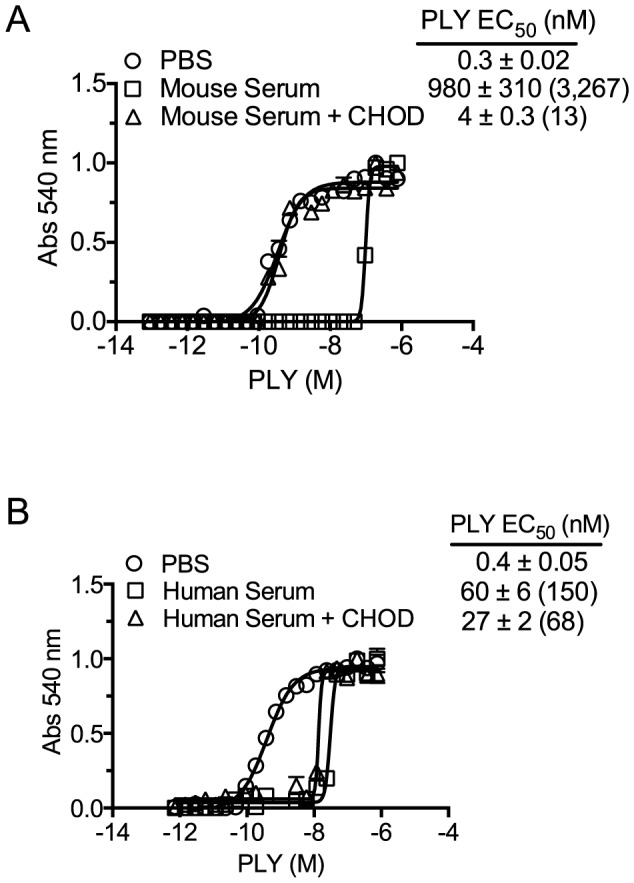
PLY requires the free 3β-hydroxyl of cholesterol to bind therefore treatment with CHOD will abolish PLY-cholesterol binding. Samples containing PBS, PBS +10% mouse serum or PBS +50% human serum were incubated with and without cholesterol oxidase (CHOD) for 30 minutes at room temperature to oxidize the 3β-hydroxyl. PLY (38 nmol/150 µl) was then serially diluted using untreated or CHOD-treated mouse (A) or human sera (B) and incubated 20′ at 37°C before RBC hemolysis was determined. The EC50 values (toxin concentration required to lyse 50% of RBCs) and the standard deviations (SD) are shown for each sample. The fold difference in the EC50 for CHOD treated and untreated samples versus PLY in the absence of serum (PBS control) is shown in parenthesis. Assays were done in duplicate; the data represent three independent experiments. The EC50 calculation included the starting serum dilutions (mouse serum was initially diluted to a greater extent, as the mouse serum was found to be significantly more inhibitory than human serum).
