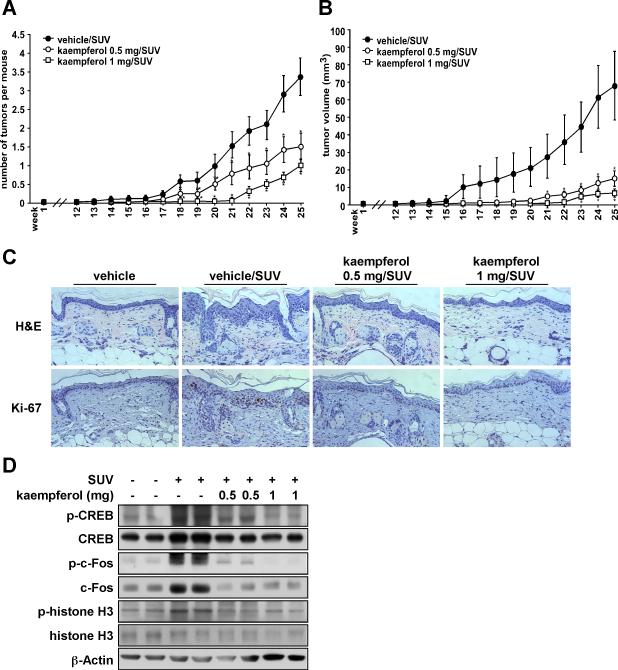
Figure 5. Kaempferol significantly suppresses SUV-induced skin carcinogenesis in a mouse skin tumorigenesis model.
SKH-1 hairless mice were treated as described in Materials and Methods. The mice in the vehicle group (n = 12) received topical treatment with acetone or 1.0 mg kaempferol only. In the vehicle/SUV-treated group (n = 24), the mice were treated with acetone before SUV exposure. The mice in the 0.5 mg/SUV or 1.0 mg/SUV groups (n = 24 each) received treatment with kaempferol (0.5 or 1.0 mg, respectively) before SUV exposure. The frequency of irradiation was set at 3 times a week for 10 weeks. The respective doses of acetone or kaempferol were applied topically to the dorsal area. Tumor incidence and multiplicity were recorded weekly until the end of the experiment at week 25. (A) Kaempferol suppresses SUV-induced average tumor number and (B) volume. Tumor volume was calculated according to the following formula: tumor volume (mm3) = length X width X height X 0.52. A and B, data are represented as means ± S.E. and differences were determined by one-way ANOVA. The asterisk (*) indicates a significant decrease compared to the vehicle/SUV-treated group (p < 0.01). (C) Kaempferol inhibits chronic inflammation and proliferation induced by SUV in mouse skin epidermal tissue. Dorsal trunk skin samples were harvested and stained with H&E (upper panels) and with an antibody to detect Ki-67 (lower panels). Representative staining shows the thickness and Ki-67 staining of the epidermis from each of the groups. Stained cells were counted from 5 separate areas on each slide and an average of 3 samples was examined per group. (D) Kaempferol inhibits SUV-induced phosphorylation of c-Fos, CREB and histone H3 in mouse skin. The expression levels of phosphorylated and total proteins were analyzed by Western blot.