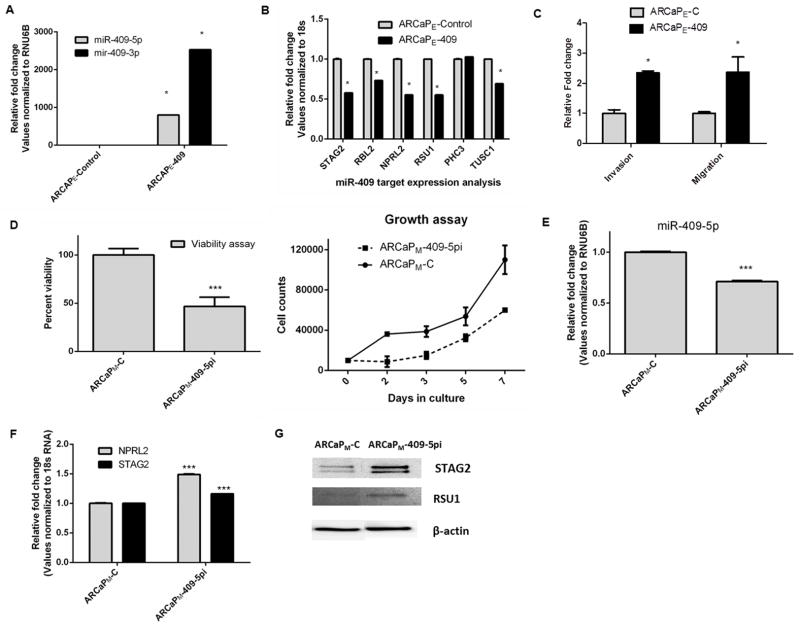
Figure 4.
Ectopic expression of miR-409 leads to increased invasiveness and aggressiveness of prostate cancer cells and conversely inhibition of miR-409 results in increased cell death in PCa cells. A, miR-409-5p and -3p expression by qRT-PCR in ARCaPE-C and ARCaPE-409 expressing PCa cells. B, RNA expression of miR-409-5p/-3p targets in ARCaPE-C and ARCaPE-409 expressing PCa cells assayed by real time PCR. (miR-409-5p mRNA targets: STAG2, RBL2, NPRL2 and RSU1and miR-409-3p mRNA targets: RSU1, PHC3 and TUSC1). C, Invasion and migration assay of in ARCaPE-C and ARCaPE-409 expressing PCa cells. D, Cell viability in ARCaPM PCa cells in response to a miR-409-5p inhibitor. Growth curve of ARCaPM-C and ARCaPM-409-5pi PCa cells. E, Expression of miR-409-5p assayed by qRT- PCR in ARCaPM-C control PCa and ARCaPM-409-5pi (miR-409-5p inhibitor transfected cells). F, RNA expression of miR-409-5p targets in ARCaPM-C control and ARCaPM-409-5pi cells assayed by qRT- PCR. (miR-409-5p mRNA targets: NPRL2 and STAG2). G, Protein expression of STAG2 and RSU1 in ARCaPM-C cells and ARCaPM-409-5pi cells. *: p<0.05 were considered to be statistically significant by t-test.