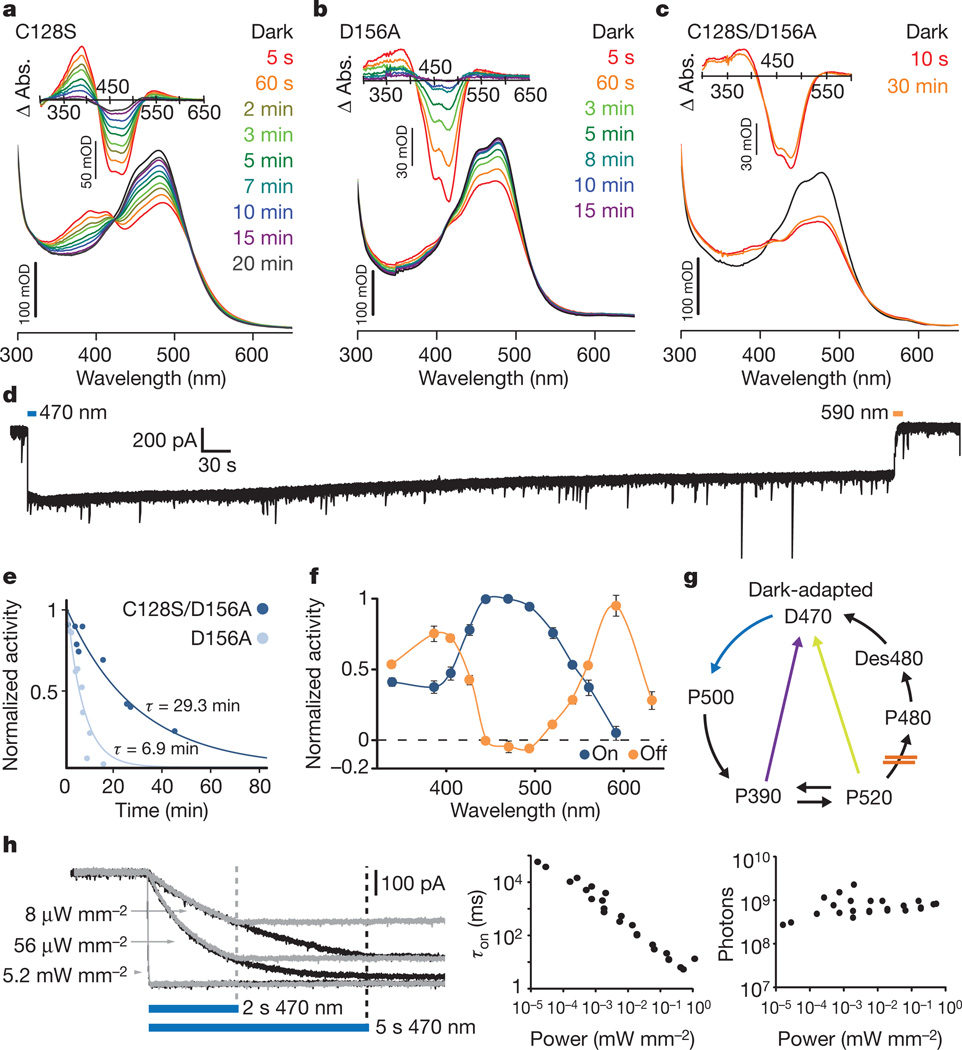
Figure 1. Kinetic and absorbance properties of a stabilized SFO.
a–c, Absorption spectra recorded after illumination with 450 nm light for 30 s. Absorption difference spectra (Δ Abs.) taken from the corresponding absorption spectra are shown in the insets. Spectra were collected at the indicated times after the end of illumination; note prominent recovery after 3 min in the single mutants, in contrast to the double mutant. d, Representative whole-cell patch-clamp recording of photocurrent in a cultured hippocampal neuron expressing ChR2(C128S/D156A) SSFO. Blue and orange bars indicate activation and deactivation light pulses. e, Monoexponential fits of photocurrent decay in cells expressing ChR2(C128S/D156A) (dark blue; τ = 29 min) or ChR2(D156A) (light blue; τ = 6.9 min). f, Activation (blue) and deactivation (orange) spectra recorded from cultured neurons expressing ChR2(C128S/D156A). g, Simplified photocycle scheme; in C128/D156 mutants the transition P520 to P480 is probably slowed down or blocked, avoiding the desensitized state Des480 which cannot be reactivated with 470 nm light. Both yellow and violet light (yellow and violet arrows) shuttle the channels to an inactive state (see Supplementary Fig. 1). h,Whole-cell photocurrent responses of a cultured neuron expressing SSFO to 470 nm light pulses of indicated power (left). Pulse lengths were 2 s (grey traces) or 5 s (black traces). Dashed lines mark light pulse termination. Apparent time constants for activation (τon) are shown on a log–log plot versus light power (n = 27 recordings from 5 cells; middle). Within this broad range of light power, the calculated number of incident photons arriving at each cell for photocurrents to reach the exponential curve constant (63% of Imax) for that cell was constant (right). Each point represents a photon number from a single recording at a given light power.