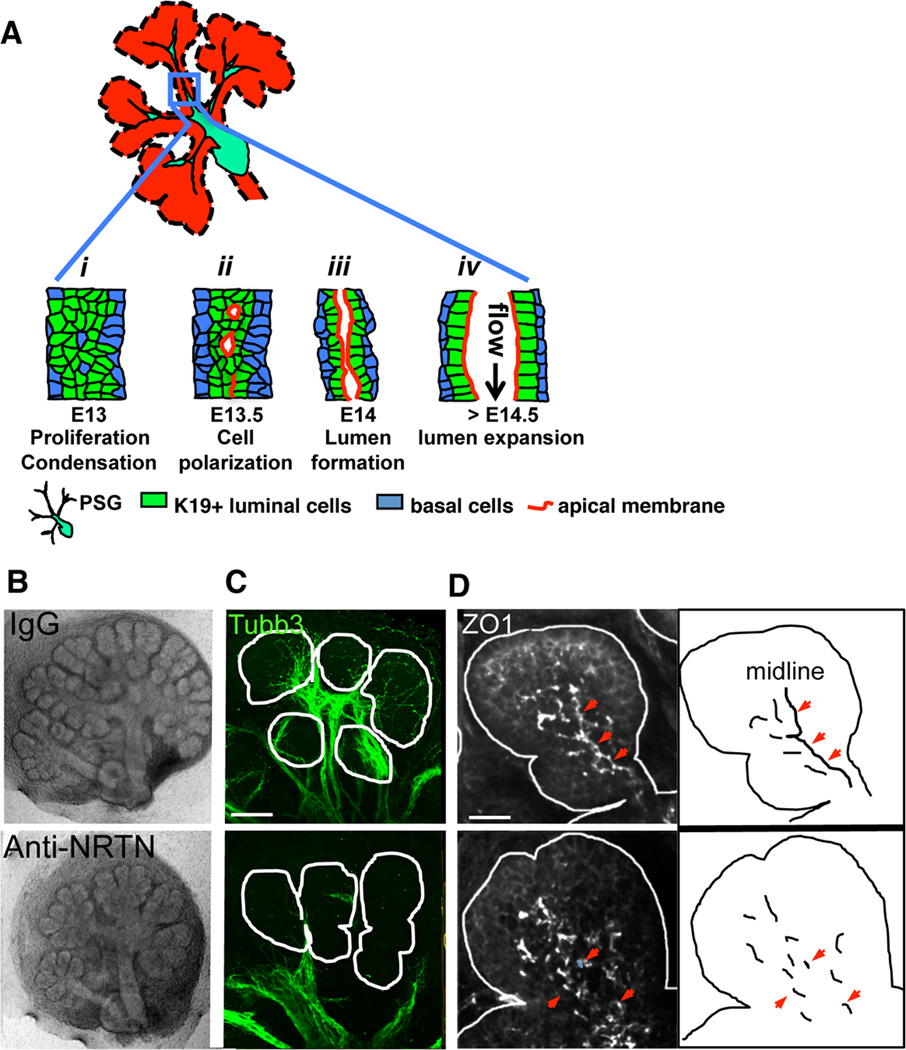
Figure 1. Parasympathetic innervation regulates lumen formation in the SMG.
(A) Schematic illustration of steps during SMG duct development: i, K19(+) luminal cells condense at ductal midline; ii, cells polarize to form microlumens with shared apical membrane; iii, microlumens coalesce to form a contiguous apical membrane bounding a luminal space; iv, lumen undergoes expansion. (B–D) E13 SMG were isolated and treated with anti-NRTN function blocking antibody for 24 h before being fixed and immunostained for nerves (C, Tubb3, green) and ZO1(+) tight junctions (D, white). Arrowheads highlight ZO1 at the ductal midline. Scale bars: C = 50 µm; D = 20 µm. C is a 30 µm projection of 1.5 µm confocal sections. D is a 12 µm projection of 1 µm confocal sections.
See also Figure S1.