FIGURE 3.
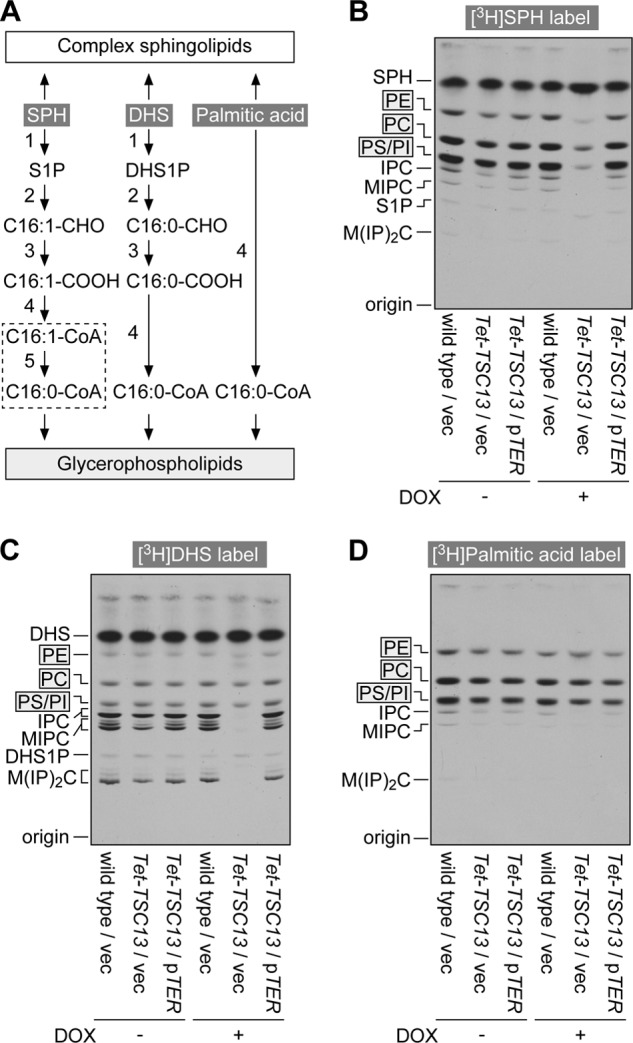
Yeast Tsc13 and mammalian TER are involved in the S1P metabolic pathway. A, metabolic pathways of SPH, DHS, and palmitic acid to sphingolipids and glycerophospholipids. Most of the enzymes are common to metabolisms of SPH and DHS (reactions 1–4). The reaction specific to the metabolism of SPH is saturation of trans-2-hexadecenoyl-CoA to palmitoyl-CoA (reaction 5; dashed box; subject of this study). The enzymes responsible for the numbered reactions are: 1, SPH kinases SPHK1 and SPHK2; 2, S1P lyase SPL; 3, fatty aldehyde dehydrogenase ALDH3A2; 4, acyl-CoA synthetases ACSL1–6, ACSBG1, ACSVL1, and ACSVL4; 5, trans-2-enoyl-CoA reductase TER identified in this study. C16:1-CHO, trans-2-hexadecenal; C16:0-CHO, hexadecanal; C16:1-COOH, trans-2-hexadecenoic acid; C16:0-COOH, palmitic acid; C16:1-CoA, trans-2-hexadecenoyl-CoA; C16:0-CoA, palmitoyl-CoA; DHS1P, DHS 1-phosphate. B–D, BY4741 (wild type) cells bearing the pAKNF315 (vector) plasmid (BY4741/pAKNF315), YRF50 (pTet-TSC13)/pAKNF315, and YRF50/pTW8 (3xFLAG-TER) were grown for 13 h at 30 °C in SC medium lacking leucine in the presence or absence of 10 μg/ml of DOX. Cells were then labeled with 0.07 μCi of [11,12-3H]SPH (B), 0.07 μCi of [4,5-3H]DHS (C), or 0.07 μCi of [9,10-3H]palmitic acid (D) for 2 h. Lipids were extracted, separated by normal-phase TLC with chloroform, methanol, 4.2 n ammonia (9:7:2, v/v), and detected by autoradiography. IPC, inositol phosphorylceramide; MIPC, mannosylinositol phosphorylceramide; M(IP)2C, mannosyldiinositol phosphorylceramide.
