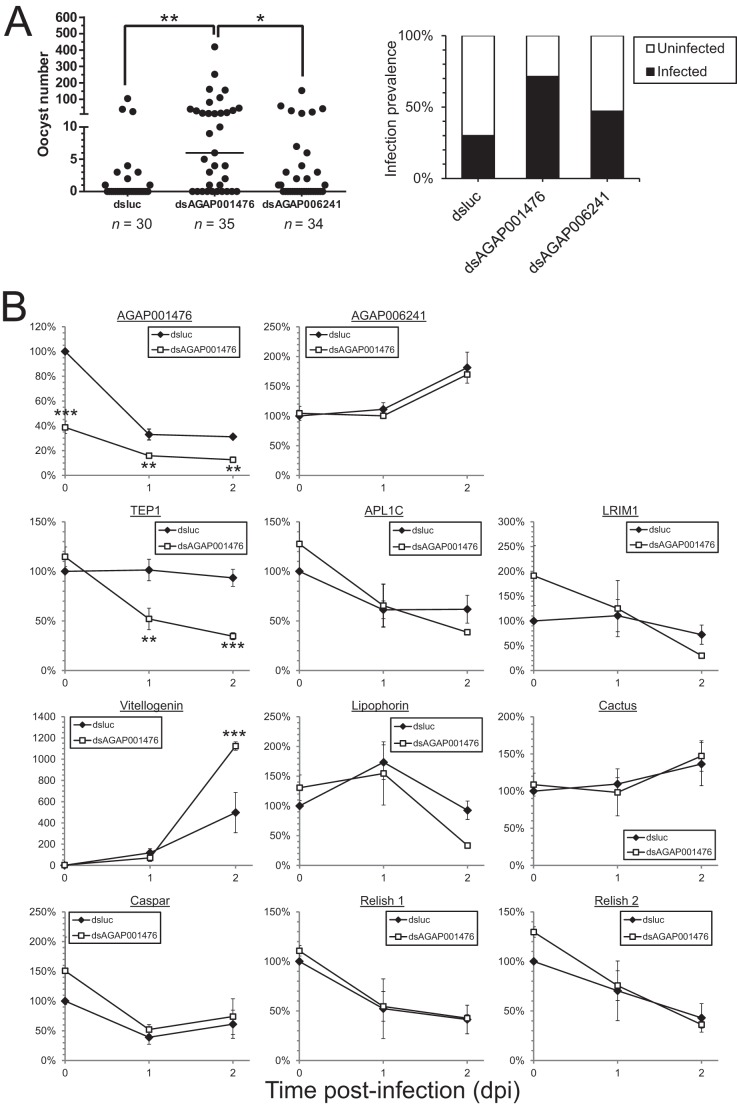
FIGURE 4.
Depletion of AGAP001476 specifically increases Plasmodium survival, which is accompanied by a decline in TEP1 and an increase in vitellogenin level. Each mosquito was injected with 0.4 μg of dsluc, dsAGAP001476, or dsAGAP006241. The oocyst number and the percentage of infected mosquitoes are shown in A. Mosquitoes receiving dsAGAP001476 had significantly more oocysts in their midguts than those receiving dsluc or dsAGAP006241. The expression levels of selected genes involved in innate immune responses and the two innexin genes of interest were assessed by qPCR and normalized against actin levels in B. Apart from a reduction in AGAP001476, mosquitoes receiving dsAGAP001476 had less TEP1 at 1 and 2 dpi and more vitellogenin at 2 dpi. Values in A represent the median from a representative experiment that was repeated three times. Values in B represent means ± S.E. of the mean compiled from four independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 by Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn's multiple comparisons test in A, and two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni's multiple comparisons test in B.